Heat pumps for home heating: types and principle of operation

Alternative heating options include the growing popularity of heat pumps. The high cost of equipment and installation of such a design does not allow some owners of private houses to minimize heating costs. They should definitely consider making a do-it-yourself heat pump.
Content
Device and principle of operation
Almost any medium that surrounds us has a certain amount of thermal energy, provided that its temperature exceeds 1° C.Why not use some of this energy to heat your own home? This is done using a heat pump.
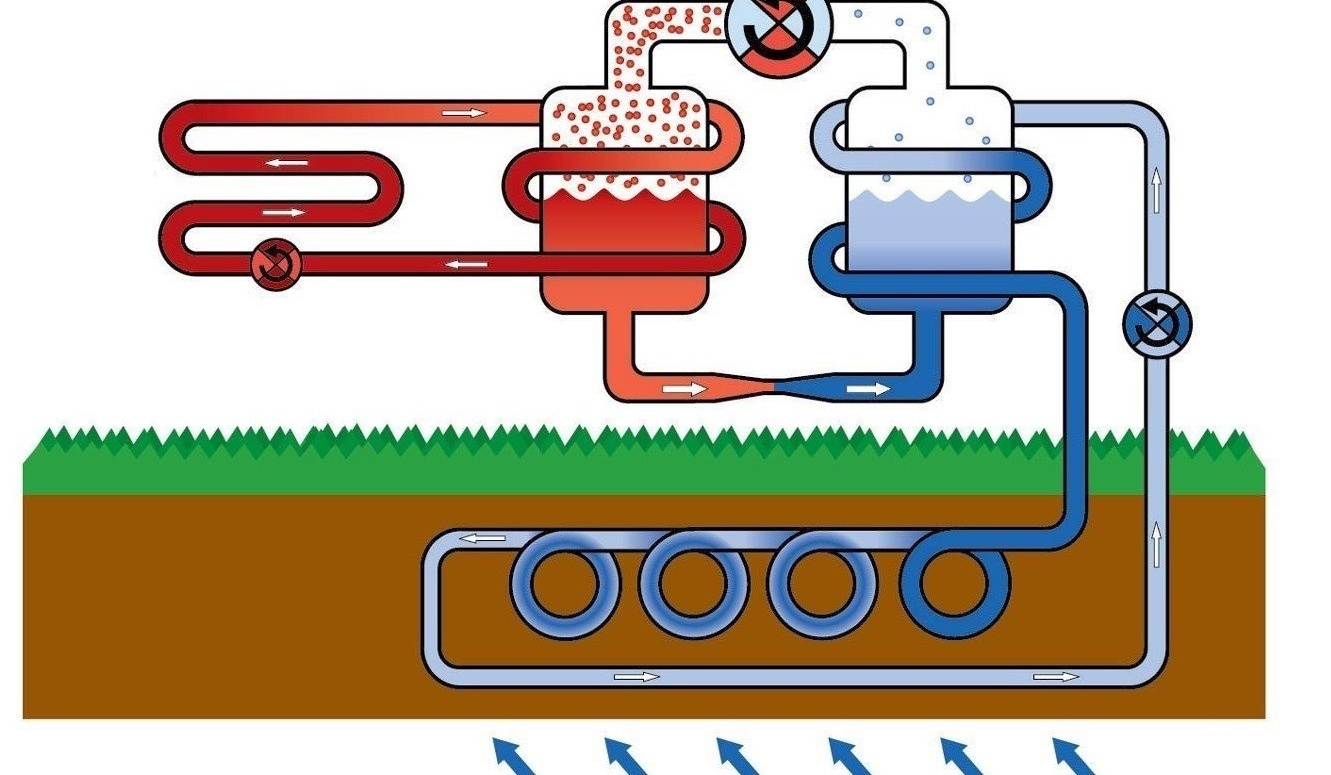
The principle of operation of a heat pump based on heat transfer from a source with a low potential of thermal energy to a heat carrier that has a higher temperature is based. In practice, it looks like this:
- The coolant enters the pipeline, located, for example, in the ground, and heats up several degrees.
- Then the heat carrier enters the heat exchanger (or evaporator) and transfers the collected heat energy to the internal circuit.
- The refrigerant (a substance with a low boiling point, which is under low pressure), which is located in the external circuit, is heated in the evaporator and converted into gas.
- Then the gaseous refrigerant enters the compressor, where it is compressed under high pressure. At the same time, the temperature of the refrigerant becomes even higher.
- Hot gas enters the condenser, where it transfers thermal energy to the coolant of the house’s internal heating system.
- After this, the refrigerant that has lost heat is returned to the system in a liquid state.
The operation of refrigeration units is based on the same principle, therefore, some types of heat pumps in the summer can be quite successfully used as air conditioners, i.e. for cooling the room.
Video: device and operation of thermal units
Types of units
A clear idea of the options for the design of heat pumps is their classification according to the type of coolant on the external and internal contours of the structure. The device can receive energy from:
- soil;
- water (body of water or source);
- air.
Inside the house, the received thermal energy can be used in the heating system, as well as for heating water or for air conditioning. Therefore, there are several types of heat pumps, depending on the combination of these elements and functions.
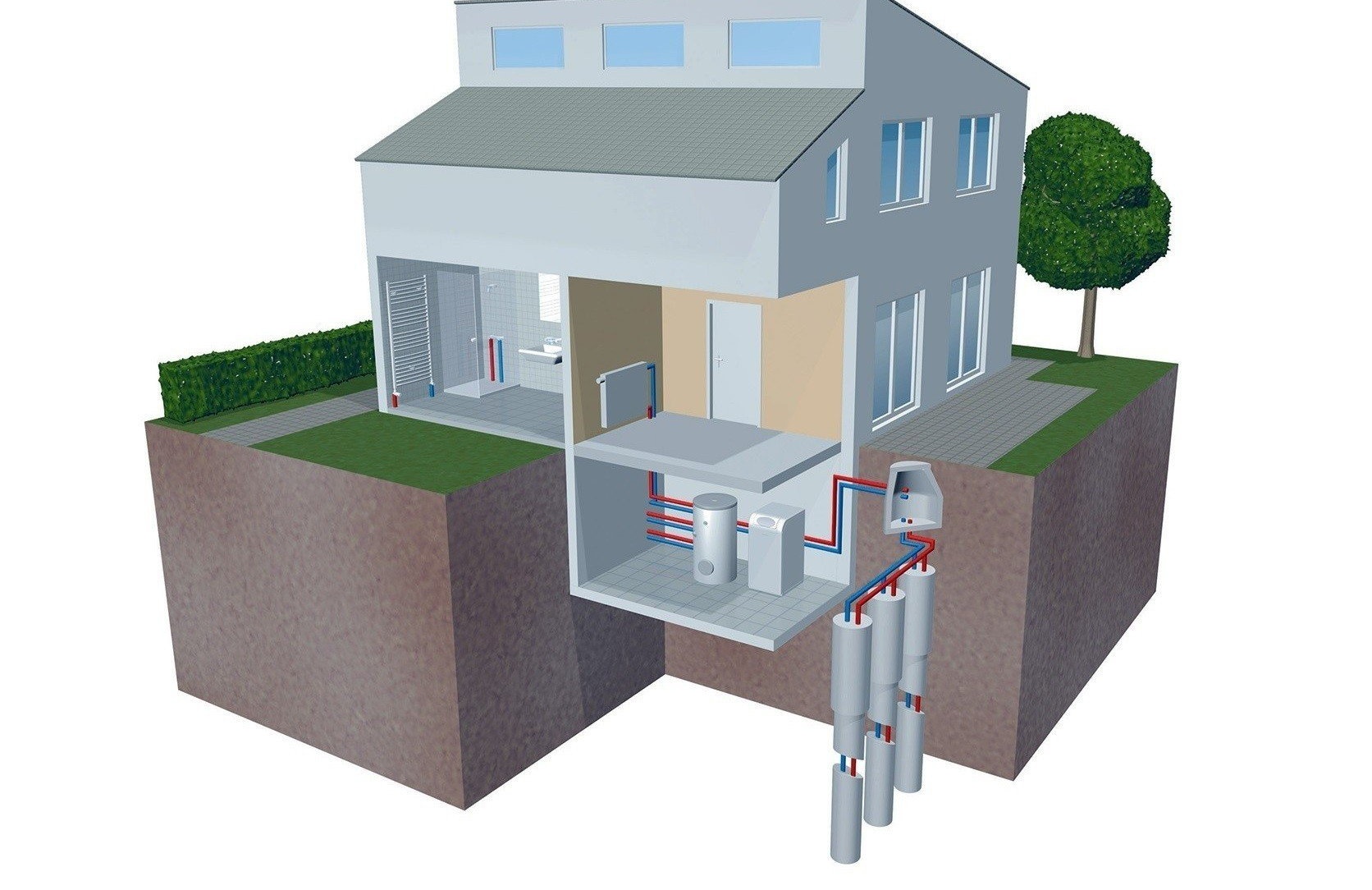
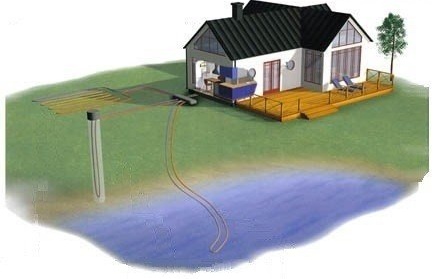
Ground-water system
Getting heat from soil is considered one of the most effective for this type alternative heatingsince already at about five meters from the surface the soil temperature remains quite constant, it is little susceptible to changes in weather conditions.
As a coolant on the external circuit, a special liquid is used, which is usually called brine. It is an environmentally friendly compound.
The outer contour of the soil-water heat pump is made of plastic pipes. You can place them in the ground horizontally or vertically. In the first case, you may need to work on a large area, from 25 to 50 square meters. m per kilowatt of pump power. The areas reserved for the horizontal collector cannot be used for agricultural purposes. Here, only a breakdown of the lawn or planting of annual flowering plants is permissible.
For the construction of a vertical reservoir, a number of wells with a depth of 50-150 meters will be needed. Since the temperature of the soil at this depth is higher and more stable, such a geothermal heat pump is considered more efficient. In this case, special depth probes are used to transfer heat.
Water-to-water pump
Heat can be an equally effective choice. pump water water, since at great depths the water temperature remains quite high and constant. As a source of low potential thermal energy can be used:
- open reservoirs (lakes, rivers);
- groundwater (wells, wells);
- wastewater of industrial technological cycles (reverse water supply).
There are no fundamental differences in the design of the soil-water or water-water heat pumps. The least cost will require the construction of a heat pump that uses the energy of an open reservoir: pipes with a coolant must be supplied with cargo and immersed in water. Using the groundwater potential will require a more complex design. An additional well may be required to discharge the water that passes through the heat exchanger.
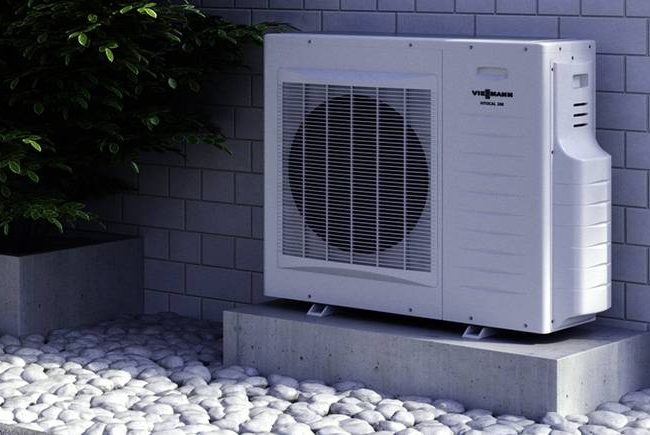
Universal option "air-water"
By efficiency heat pump air water inferior to other models, because in the cold season, its power is significantly reduced. However, for its installation does not require complex work on excavation or the construction of deep wells. It is only necessary to select and install suitable equipment, for example, directly on the roof of the house.
The undoubted advantage of this design is the ability to reuse heat that leaves the premises heated by the heat pump with exhaust air or water, as well as smoke, gas, etc. In order to compensate for the lack of power of the air heat pump in winter, alternative heating options should be considered.
The least expensive option may be an air-to-air heat pump, the construction of which does not require complicated work to create a traditional water heating system in rooms.
Read more about this type of heat pump in our article:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/otoplenie/alt_otoplenie/teplovoj-nasos-vozdux-vozdux.html.
Advantages and disadvantages of the system
Installation of a heat pump at home and its inclusion in the heating system or the creation of a full-fledged heating station will solve a number of pressing problems and has the following advantages:
- it is an autonomous heating system, the only centralized element of which is the connection to the power grid;
- this method can significantly save on expensive energy carriers, which are traditionally used for heating and significantly reduce utility costs.The average heat conversion coefficient is 3.5 - 4.5. From 1 kW of electricity, the pump generates from 3 to 7 kW of heat. These are the highest rates among all types of boilers running on any fuel;
- the system is safe for human health and for the environment. It helps to save the planet’s non-renewable energy resources;
- fire safety and non-flammability of parts. This boiler does not overheat, does not explode, does not burn, does not emit carbon monoxide;
- one pump can produce both heat and cold, providing the necessary microclimate in the house, as well as heating water for domestic needs;
- durability - according to the experience of European residents, the service life of the equipment is 20-50 years;
- comfort and silent operation. The system is controlled by automation;
- installation of the pump does not require approvals, which are necessary during installation, for example, of gas equipment.
In Norway and Sweden, 95% of all homes are heated by heat pumps.
The disadvantages include:
- the relatively high cost of installation and the pump itself, the payback of such a system depends on the intensity of its operation;
- the need to attract specialists and use special drilling and other equipment to equip a geothermal pump with a vertical circuit, the depth of which can reach 200 m.
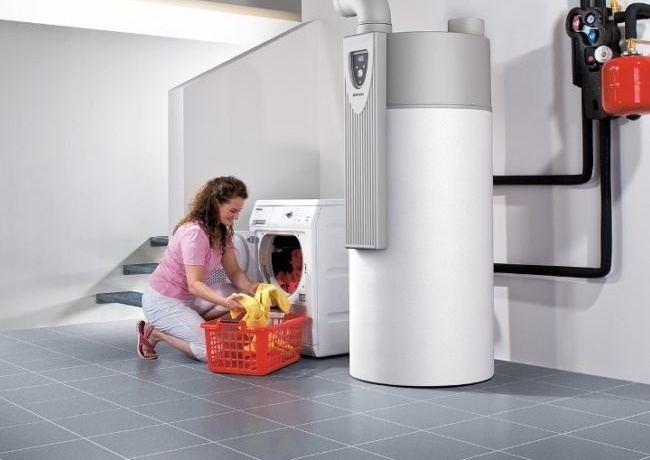
How to make a DIY heat pump
Using heat pumps to heat your home is profitable and convenient. Experience shows that in private houses with a living area of more than 400 square meters. m such a design will pay off within a few years of operation, despite the high cost. Owners of houses with more modest sizes successfully develop and install heat pumps of their own design. Here are some guidelines for creating these useful devices:
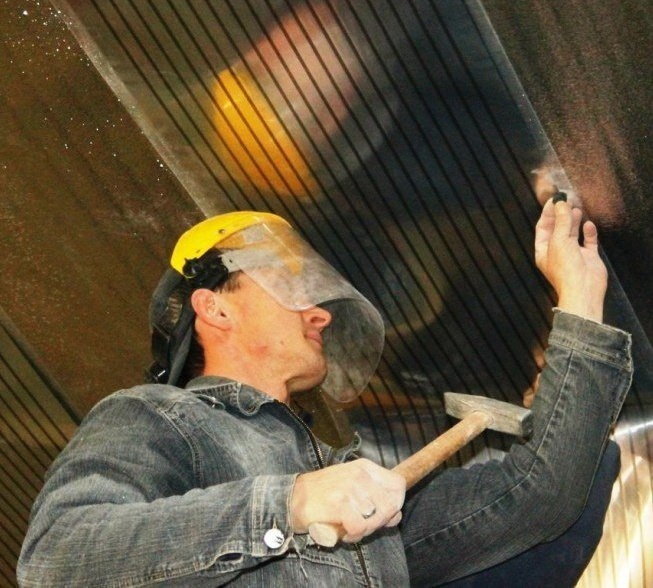
- First you need to take care of the purchase of a compressor, for example, designed for air conditioning. Usually it is fixed to the wall.
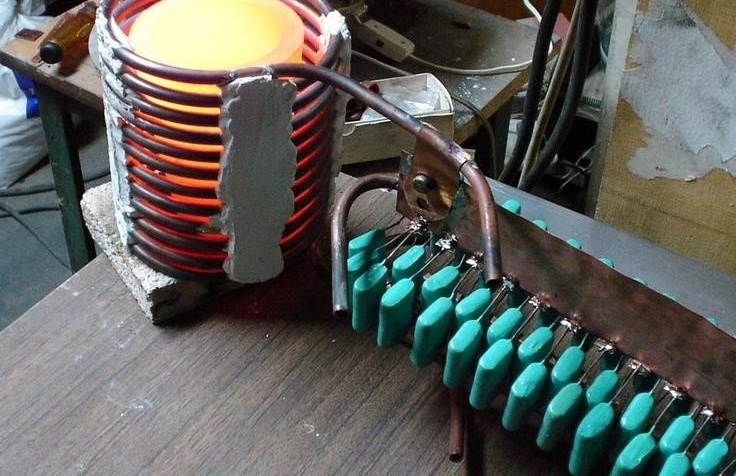
- another important part of the design - the capacitor - can be done independently. To do this, you need to make a coil from a copper pipe (at least 1 mm thick), which is placed in a metal or plastic case. A suitable size tank is suitable as a housing. After the coil is installed, the halves of the tank are welded, mounting the necessary threaded connections. The evaporator is also usually mounted on the wall. To make a high-quality coil, you can wrap a copper plumbing pipe around an object of a suitable diameter, a gas cylinder is quite suitable. To ensure that the distance between the turns is the same, use a perforated aluminum corner, on which the coils of the coil are fixed.
- final installation of this equipment: soldering of a copper pipe, injection of freon, etc. - should be performed only by a qualified specialist. Inept actions can damage the equipment, in addition, they are associated with a high probability of personal injury.
- after that, the design is connected to the internal heating system of the house.
- then the external circuit is installed and connected, the features of this process depend on the type of heat pump.
Before starting the heat pump, it will not hurt to diagnose the condition of the house wiring and meter. Old and outdated equipment must be replaced. Acceptable power meter is at least 40 amperes.
Unfortunately, not every heat pump for home heating meets the expectations of the owners. Most often this is due to the lack of correct thermodynamic calculations. The result is a system with insufficient power or the costs of excessively powerful equipment are unreasonably rising. To choose a system with a suitable capacity, it is necessary to take into account the heat loss of the building, as well as many other characteristics. Such calculations should be entrusted to a design engineer.
Cost-effectiveness and feasibility of using heat pumps
In order to achieve significant savings on the heating budget for many years, it is necessary to spend significant funds at the design and installation stage. The payback of such a heating system is delayed in time, it depends on operating conditions.
Energy taken from the environment does not require payment and does not end there.
If the floor and walls are properly insulated in the house, then the heat pump will work as efficiently as possible. Heat loss should not exceed 100 watts per 1 square. meter.
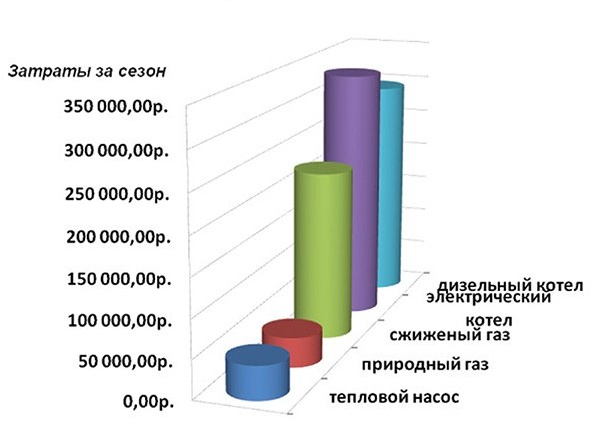
The following is a comparison of heating costs when using various energy sources.
It is very beneficial to include the pump in a system of underfloor heating or walls, where the operating temperature is approximately 40 degrees. An indicator of savings can be considered the absence of overheating of the heating circuit and freezing of the coolant when the pump is turned off, which improves the reliability of the system and reduces the risk of an accident and the frequency of preventive and repair work.
The cost of installing such a system depends on several factors:
- the area of the heated premises of the house;
- variety of pump design;
- heating systems and pipes laid in the house;
- indicators of heat loss.
For a small house of 130 square meters. m when installing a pump with a soil heat intake, the cost of the equipment will be 450,000 p., and the installation will pull 300,000 p.
The air-water pump will cost 300 00 r., The installation will be 80 000 r. This is the most inexpensive option.
The maximum costs will be required for deep drilling with a low freezing point and for a large area of the house, for example, 400 square meters. m. Equipment will cost 800,000 p., and installation - 360,000 p. Costs include all design and excavation, ground works and all elements of the pump and heating system.
Material updated 03.03.2018






24 comments