Types of heaters and calculation of their power for ventilation

A heater, or a channel heater, is the general name for pipe devices through which air masses are heated indoors. In such an installation, hot water, air or steam can circulate.
Content
What is a heater and what is it for?
It is a kind of heat exchanger, in which the heat source is the air currents in contact with the heating elements. Using the device, the supply air is heated in ventilation systems and drying equipment.
The device to be mounted can be represented as a separate module or be part of a monoblock ventilation unit. The scope is presented:
- the initial heating of the air in the supply ventilation systems with air flow from the street;
- secondary heating of air masses during recovery in supply and exhaust type systems that regenerate heat;
- secondary heating of air masses inside separate rooms to ensure an individual temperature regime;
- heating the air to supply it to the air conditioner in the winter;
- backup or additional heating.
The energy efficiency of a channel air heater of any design is determined by the coefficient of thermal return under conditions of certain energy costs, therefore, with significant indicators of thermal return, the device is considered to be highly efficient.
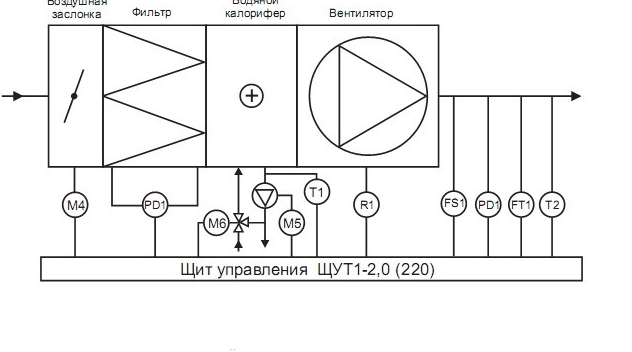
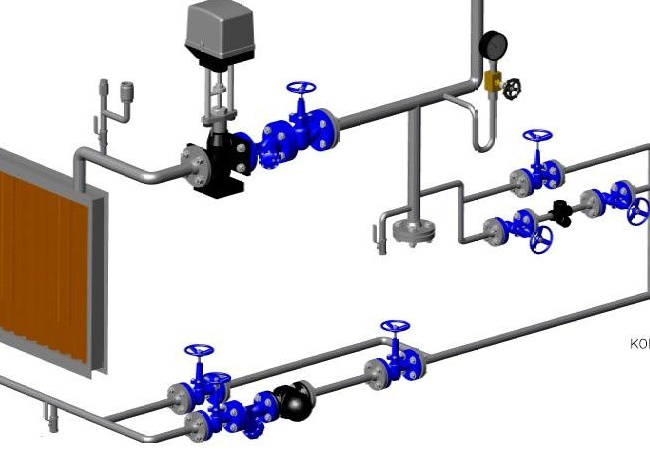
The piping in the supply ventilation system of the control reinforcing cage is carried out by means of two-way valves in the city network, as well as three-way valves when using a boiler room or boiler. Using the installed strapping unit, the performance of the equipment used is easily controlled, and the risk of freezing in winter is minimized.
Views
Heating and ventilation equipment is represented mainly by water and steam appliances.
Preference is most often given to water heaters, which differ:
- surface shape. They can be smooth-tube and ribbed, lamellar and spiral-wound;
- the nature of the movement of the thermal carrier. Single-pass and multi-pass air heaters.
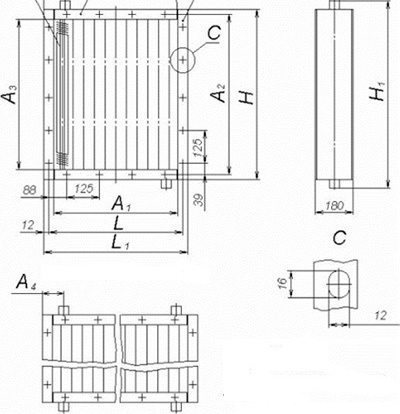
Depending on the size of the heating surface, all water and steam devices are represented by four models: the smallest (SM), small (M), medium (C) and large (B).
Water
Water-type heaters provide heating of the air inside the ventilation duct to a comfortable temperature by means of the energy of the heat carrier, constantly circulating in the radiator part of the equipment. Liquid coolants are not inferior in their main characteristics to analogs of the electric type, but they are characterized by increased energy consumption and some installation complexity, so their installation should be carried out by specialists.
The principle of operation is based on the presence in the design of empty copper links or based on copper alloys of a coil arranged in a checkerboard pattern. The device also has aluminum plates designed for heat recovery. Inside the copper coil, the heated liquid, represented by water or glycol solution, moves, as a result of which heat is transferred to the air flows from the supply system.
The main advantages of water air heaters in ventilation systems include the high efficiency of heating large areas, due to its structural features.
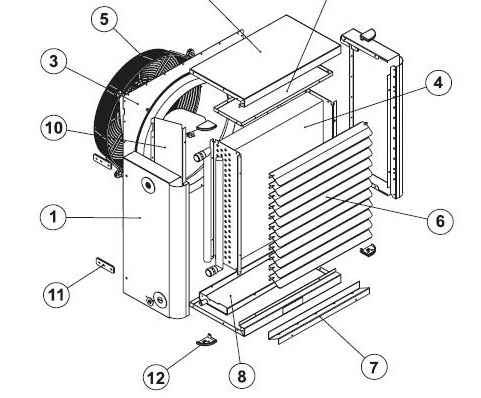
- side part of the body;
- upper and lower panels of the case;
- ventilation pipe on the rear panel;
- heat exchanger;
- motor support grill;
- orientable type blades;
- additional condensate tank;
- main condensate tank;
- the upper part of the heat exchanger body;
- air duct
- device fixing brackets;
- plastic squares.
The main disadvantage is the high risk of freezing of the device in conditions of sharply negative temperatures, which is explained by the presence of water in the system and requires mandatory protection against icing.
They are represented by metal tubes with a ribbed outer part, which increases the efficiency of heat transfer. Duct heaters, through whose pipes the heated thermal carrier moves, and air masses move and heat outside, it is advisable to mount in rectangular ventilation systems.
Steam
They are in demand by industrial enterprises with an excess of steam, which allows to meet the technological needs of the device. The heat carrier in such a device is represented by steam supplied from above, and during its passage through the working elements of the heat exchanger, condensate forms.
All currently produced steam heat exchangers are required to pass a leak test by means of dry air supplied with a pressure of 30 bar when the device is immersed in a tank filled with warm water.
The advantages of devices in the air conditioning and ventilation system include quick heating of the room, which is explained by the design of such a device.
- board with pipes;
- lateral flap part;
- a heating element;
- gasket.
A tangible minus of the steam channel heater is the mandatory availability of equipment that continuously generates steam.
Electric
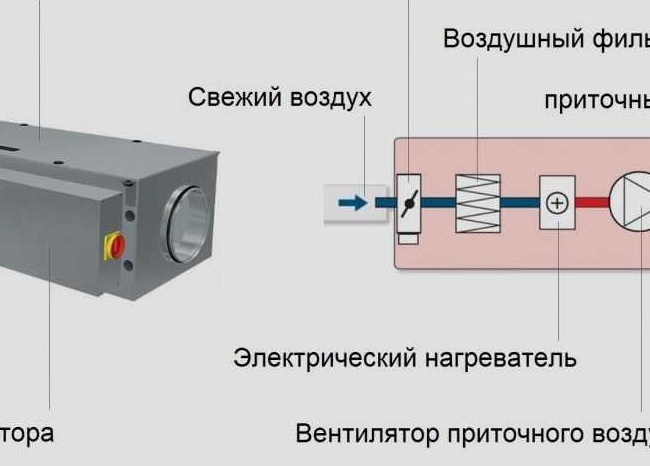
It is economically feasible to equip the least powerful ventilation systems with conventional electric heaters. The principle of operation of the device is based on the passage of air flows supplied through the supply ventilation system through the heating elements that give off part of the thermal energy. Heated air is supplied to the room, and protection from any overheating is realized by bimetallic thermal switches.
Such devices absolutely do not need to connect too complex or professional communication systems, therefore they are connected to existing power supply lines, which is a definite plus.
The internal device is represented by pipe-type electric heaters, which ensures the most efficient heat exchange with the surrounding air currents.
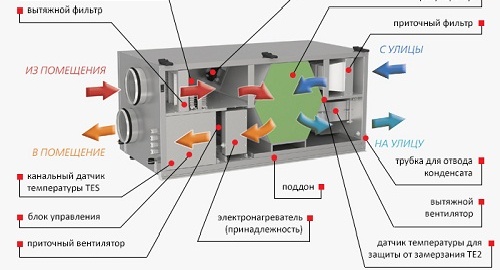
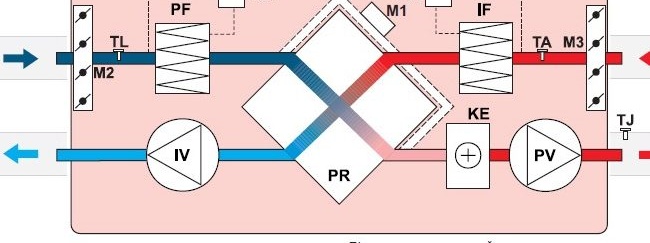
- IV - ventilation element for exhaust air;
- PV - ventilation element for supply air;
- PR - plate type heat exchanger;
- KE - electric heating element;
- PF - filter system for fresh air;
- IF - filter system for exhaust air;
- TJ - temperature sensor for supply air;
- TL - temperature sensor for fresh air;
- TA - temperature sensor for exhaust air;
- M1 - air valve type motor;
- M2 - valve for fresh air currents;
- M3 - valve for exhaust air flows;
- PS1 - differential pressure switch for supply air flows;
- PS2 - differential pressure switch for exhaust air flows.
The use of electrical appliances can only be justified in a ventilated room, the area of which is less than 100-150 m2. Otherwise, the level of electric energy consumption will be too high.
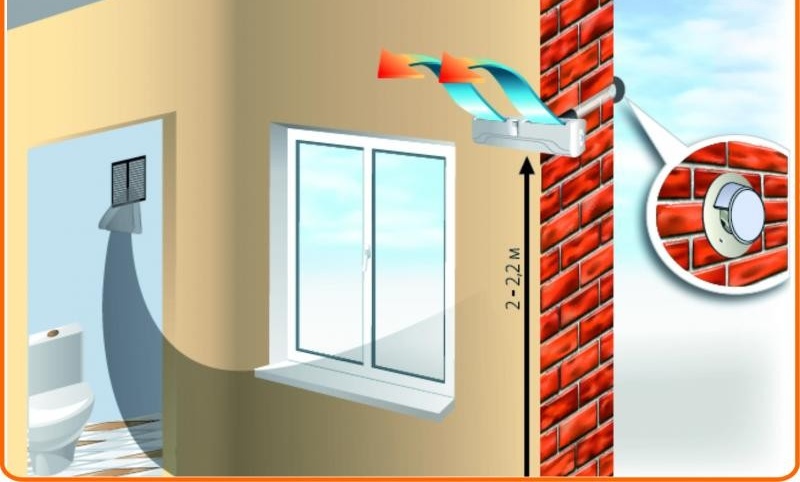
High-quality ventilation in the house will relieve dampness and stagnant air. In the next article, you will learn more about the installation of a supply and exhaust system:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/ventilyaciya/pritochno-vyityazhnaya-ventilyatsiya-v-chastnom-dome.html.
Power calculation
Obtaining air with the necessary temperature indicators involves the correct calculations and the correct choice of a device for ventilation of the supply type. Even though modern water devices with a thermal carrier in the form of hot water are especially popular, when choosing a device of any type, it is initially required to determine its power on the basis of the initial data presented:
- the volume of heated supply air masses in m³ / h or kg / h;
- temperature indicators of the initial air masses equal to the calculated temperature of the street air in a particular region;
- the preferred temperature regime of air flows after heating;
- temperature graph of the thermal carrier used for heating.
A simplified determination of the power of the channel heater is carried out in accordance with a simple formula:
P = 0.34 × Q × T
Q - ventilation system capacity in m3/hour;
T is the difference in temperature inlet and outlet in the ventilation duct.
Table: power calculation for the main parameters of the ventilation system
| Productivity, m3 | Power of heating element, kW |
| 80 | 1,2 |
| 160 | 2,4 |
| 240 | 3,6 |
| 330 | 4,8 |
| 510 | 7,5 |
| 730 | 10,8 |
| 1020 | 15,0 |
| 1520 | 22,5 |
| 2030 | 30,0 |
For example, the air volume in a room measuring 20 m2 with a ceiling height of 300 cm, equal to 60 m3therefore single air exchange is 60 m2/hour.
Table: power indicators of electric, steam and water channel heater
| Indicators | t air inlet oC | |||||||||
| 0 | -5 | -10 | -15 | -20 | -25 | -30 | -35 | -40 | -45 | |
| Power, kWt | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.21 |
The supply air supplied to the room from the street requires processing in order to obtain regulatory parameters. Air masses can be processed by filtration, heating, cooling and humidification. The supply air flows are heated inside the special heat exchange equipment represented by heaters.
Liquid duct heaters are today the most popular, widely used in most ventilation systems. The fluid type fluid is constantly moving in the opposite direction to the air flow, which provides efficient and inexpensive heating, which significantly saves energy and supports optimal microclimatic conditions in any type of premises.