Aluminum heating radiators: technical overview + selection tips

Modern aluminum heating radiators have appeared on the market relatively recently, but they are already confidently crowding out the good old cast-iron batteries from private and multi-apartment buildings. Skeptics doubt: can lightweight aluminum effectively replace reliable and heavy cast iron? Experience shows that this is entirely possible. An overview of the production and design features of aluminum batteries will help ensure their high reliability. It is also worth paying attention to some of the shortcomings of these devices in order to properly prepare for possible unpleasant surprises.
Content
Why is such a radiator better than others?
Aluminum - metal is light, fusible, easy to process, with excellent heat dissipation, etc. It is perfect for creating heating appliances. The advantages of aluminum radiators are many:
- high heat transfer at relatively small sizes;
- low weight of the structure compared to cast iron counterparts, which reduces the cost of transportation and installation;
- low inertia of heating, i.e., the ability to respond to a change in the temperature of the coolant for a short period of time;
- optimal ratio “thermal power / cost”;
- attractive appearance;
- powder coating resistant to external corrosion (such batteries almost never need to be repainted);
- convection heating method that prevents the accumulation of a large amount of dust between sections.
Please note that, theoretically, aluminum radiators can be painted with high-temperature enamel of any color, although in practice the consumer is usually offered white sections that are in perfect harmony with any interior. Fans of the original design should be interested in the opportunity to order spectacular colored radiators or use special decorative grilles.

Aluminum radiator sections can be painted in any color or a suitable photo image can be applied. If the painting is carried out in the factory, it will last as long as the radiator itself
Read about methods of masking radiators in our material:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/otoplenie/radiatory/kak-i-chem-zakryt-batareyu-otopleniya.html.
When choosing aluminum radiators for your home, you should be aware of the disadvantages characteristic of structures of this type. Their main enemies: bad coolant and water hammer. Poor quality or improper preparation of the coolant can cause electrochemical corrosion of the device. To cope with this problem, a protective polymer coating is applied to the inside of the radiator. This is especially true for subscribers of the central heating system, which simply cannot somehow significantly affect the composition of the coolant in the system.
Sudden water shocks that occur when checking the condition of the heating system can damage aluminum radiators. Given this drawback, manufacturers increased the value of the working pressure of the radiators from the previous 10 atm. up to 16 atm. When choosing a suitable design, you need to pay attention to this point.
Owners of private homes with autonomous heating are more protected from breakdowns. They can monitor the condition of the coolant and the absence of excess loads during system startup, which can significantly increase the life of the radiators.
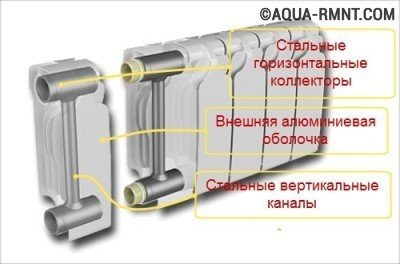
This diagram illustrates the structure of an aluminum radiator. This design is strong enough, while allowing you to get the maximum heat from the coolant
Another important point is the connection of aluminum structures with pipes of antagonist metals: steel or copper. The combination of aluminum-copper or aluminum-steel is a fine soil for the occurrence of electrochemical corrosion. To eliminate this unpleasant phenomenon, it is recommended to use special chrome-plated, cadmium-plated or nickel-plated through plugs when installing aluminum heating radiators.
Production methods and assembly features
According to the production method, aluminum radiators are cast or extruded. In the first case, the section is completely and immediately cast under pressure. In the second case, sections are made by extrusion of a ductile aluminum alloy, and the upper and lower parts of the collector are injection molded. Then all parts of the device are connected using a special adhesive.
The process of ebb radiators looks something like this:
- parts of the mold are connected under pressure in an injection machine;
- alloy is fed into the chamber with limited volume;
- the alloy through the injection channels is pushed into the mold using a plunger;
- the melt cools and crystallizes;
- the mold opens and the hot cast is stacked for final cooling;
- flashing is carried out and the neck is welded;
- the tightness of individual sections is checked;
- the design is alternately immersed in baths with anticorrosive compounds to protect the inner surface;
- drying and cooling of the structure;
- sections are painted with powder enamel using an electrostatic field;
- the radiator is assembled and again checked for strength.
The technology for the production of radiators from different manufacturers may vary, depending on new developments and patents received. This takes into account the cooling rate of the aluminum alloy, the rate of its distribution in shape, alloy shrinkage during crystallization, etc. Primary or secondary aluminum can be used to produce sections. Products made from primary raw materials are considered more durable.
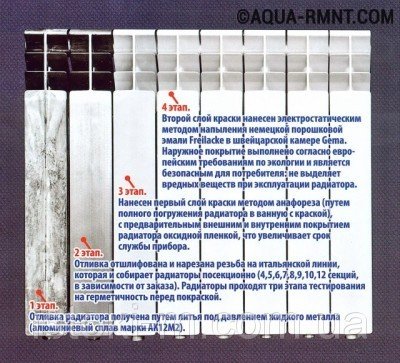
The diagram provides a description of the four stages of assembly of a multi-section aluminum radiator. Modern technologies make the design very durable and resistant to various external influences
European manufacturers most often use the injection method, since it allows for higher structural strength. Although the total strength of extruded radiators is slightly higher and amounts to 10-40 atm. against 16-20 atm. cast models, they show frequent breakdowns at the junctions of individual parts.
The company Rovall (Italy) successfully practices a hybrid production method. Two or three sections of a block radiator are cast at once, which are then connected to the collector blocks by electrochemical welding. To connect the blocks using a set of steel nipples and special gaskets, which allows you to adjust the size of the structure depending on the heating area.
A unique development is the Faral Trio HP two-channel radiator. It quite successfully withstands a burst pressure of about 60 atm and has a high heat transfer - up to 212 watts.The manufacturer uses a special form of hot aluminum alloy, and special round knives are used to form channels.
Note! According to ABOK standards (2005), the burst pressure of an aluminum radiator should be three times higher than the operating pressure of the device. If the manufacturer claims a working pressure of 16 atm, then the burst pressure should be at least 48 atm. Typically, for cast radiators, this figure is 45 atm.
Before installation, the aluminum radiator must be properly assembled. A variant of such an assembly is presented in the video material:
Aluminum and copper boiler heat exchanger
Some installers are sure that aluminum batteries cannot be combined with a boiler that uses a copper heat exchanger. Indeed, aluminum and copper are considered incompatible galvanic pairs. If you connect these metals directly with each other, copper will attract aluminum ions, as a result of which the aluminum structure will quickly be simply destroyed.
However, in heating systems it is simply impossible to imagine direct contact of the radiator with the copper coil of the boiler. Most often, they are used to connect polypropylene pipes. Since copper and aluminum do not come into contact, ion leakage is completely ruled out. The life of the radiator will not change, regardless of the metal from which other elements of the heating system are made.
Calculation of the required number of sections
It is believed that one section of the radiator is enough to heat 1.5-2 sq.m. the area of the room. In practice, this approach is not always true, since other information about the room should be taken into account, such as:
- location of the room (corner room or not);
- degree of freezing of the outer wall;
- the thickness of each wall;
- the presence and characteristics of double-glazed windows;
- type of roofing material;
- roof condition, etc.
The most important technical characteristics of aluminum heating radiators include data such as heat transfer and working pressure. Heat transfer characterizes the amount of heat that can be obtained using one radiator section. This indicator is correlated with the operating temperature of the heating system.
As a guide, you can use our calculator to calculate the required number of sections:
Fields are filled incorrectly. Please fill in all fields correctly to calculate the number of sections
For advertising purposes, manufacturers often provide not-so-correct information about the heat transfer of their products. For example, indicate that at an operating temperature of 70 degrees Celsius each section gives 210 watts of heat. However, 70 degrees is too high, usually the operating temperature in the system rarely exceeds 60 degrees. When buying, you should consider this point. Most often, with dimensions of 100 * 600 * 80 mm, the correct heat transfer data is 180 W. Under standard conditions, this amount of heat is enough to heat 1.4 sq.m. premises.

To control the operation of an aluminum heating radiator, special valves with a thermostat are mounted, which allow changing the degree of heating of air in a living room
Before choosing and installing radiators, you need to make a careful calculation of the heating system in order to eliminate heat loss. How to do this, read our article:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/otoplenie/raschety/teplovoj-raschet-sistemy-otopleniya.html.
The operating pressure reflects the force of the coolant that the radiator can withstand.As mentioned above, in most modern aluminum batteries, this figure is 16 atm. The working pressure in the system with centralized heating of multi-storey buildings rarely exceeds 6 atm. It would seem that a significant margin of safety has been laid, however, sometimes radiators fail at high loads. This usually happens during the system check before the start of the heating season. It is recommended to choose high-quality radiators and monitor compliance with the installation rules. In this case, the probability of damage will be minimized.



1 comment