Calculation of the number of sections of heating radiators

The correct calculation of the sections of heating radiators is a rather important task for each homeowner. If an insufficient number of sections is used, the room will not warm up during the winter cold, and the purchase and operation of too large radiators will entail unreasonably high heating costs.
For standard rooms, you can use the simplest calculations, but sometimes it becomes necessary to take into account various nuances in order to get the most accurate result.
Content
General calculation guidelines and requirements
- Dimensions of the room to be heated;
- Type of battery, material of its manufacture;
- The power of each section or solid battery, depending on its type;
- Maximum allowable number of sections selected radiator model;
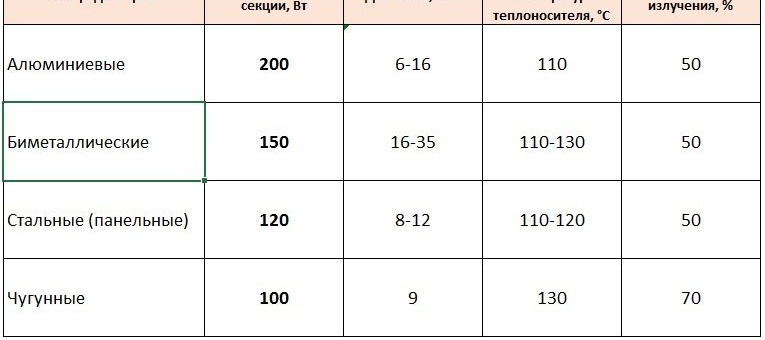
According to the material of manufacture, radiators are divided as follows:
- Steel. These radiators have thin walls and a very elegant design, but they are not popular due to numerous shortcomings. These include low heat capacity, rapid heating and cooling. When water shocks occur at the joints, leakage often occurs, and low-cost models quickly rust and do not last long. Usually there are solid ones, they are not divided into sections, the power of steel batteries is indicated in the passport.
- Cast iron radiators are familiar to everyone since childhood, this is a traditional material from which they are made long-lasting and have excellent technical characteristics of the battery. Each section of the Soviet-era cast-iron accordion produced 160 W heat transfer. This is a prefabricated structure, the number of sections in it is unlimited. Can be both modern and vintage design. Cast iron perfectly holds heat, is not subject to corrosion, abrasive wear, compatible with any coolants.
- Aluminum batteries are lightweight, modern, have high heat dissipation, due to their advantages they are gaining more and more popularity among customers. The heat dissipation of one section reaches 200 watts, they are produced by solid designs. Of the minuses, oxygen corrosion can be noted, but this problem is solved using anodic oxidation of the metal.
- Bimetal radiators consist of internal collectors and an external heat exchanger. The inside is made of steel and the outside is made of aluminum. High heat transfer rates, up to 200 W, are combined with excellent wear resistance. The relative minus of these batteries is the high price compared to other types.
How to calculate the number of sections of heating radiators for a room
There are several ways to make calculations, each of which uses certain parameters.
By area
A preliminary calculation can be done, focusing on the area of the room for which radiators are bought. This is a very simple calculation, which is suitable for rooms with low ceilings (2.40-2.60 m). According to building codes, heating will require 100 watts of thermal power per square meter of space.
We calculate the amount of heat that will be needed for the entire room. For this, we multiply the area by 100 W, i.e., for a room of 20 square meters. m the estimated thermal power will be 2,000 watts (20 sq. m * 100 watts) or 2 kW.

The correct calculation of heating radiators is necessary to guarantee a sufficient amount of heat in the house
This result must be divided by the heat transfer of one section specified by the manufacturer. For example, if it is equal to 170 W, then in our case the required number of sections of the radiator will be: 2,000 W / 170 W = 11.76, i.e. 12, since the result should be rounded to the nearest whole number. Rounding is usually carried out in the direction of increase, however, for rooms in which heat loss is below average, for example, for the kitchen, you can round down.
Be sure to consider the possible heat loss depending on the specific situation. Of course, a room with a balcony or located in the corner of the building loses heat faster. In this case, you should increase the value of the calculated heat capacity for the room by 20%. About 15-20% should increase the calculations if you plan to hide radiators behind the screen or mount them in a niche.
And to make it more convenient for you to read online, we made this calculator for you:
Fields are filled incorrectly. Please fill in all fields correctly to calculate the number of sections
By volume
More accurate data can be obtained by calculating the sections of heating radiators taking into account the height of the ceiling, i.e., according to the volume of the room. The principle here is about the same as in the previous case. First, the total heat demand is calculated, then the number of radiator sections is calculated.

If the radiator is hidden by the screen, you need to increase the room's need for thermal energy by 15-20%
According to the SNIP recommendations, for heating every cubic meter of living space in a prefabricated house, 41 watts of thermal power is needed. Multiplying the area of the room by the height of the ceiling, we obtain the total volume, which we multiply by this standard value. For apartments with modern double-glazed windows and external insulation, less heat will be needed, only 34 watts per cubic meter.
For example, we calculate the required amount of heat for a room of 20 square meters. m with a ceiling height of 3 meters. The volume of the room will be 60 cubic meters. m (20 sq. m * 3 m). The calculated thermal power in this case will be equal to 2 460 W (60 cubic meters * 41 W).
And how to calculate the number of radiators? For this, it is necessary to divide the data obtained by the heat transfer of one section indicated by the manufacturer. If we take, as in the previous example, 170 W, then for the room you will need: 2 460 W / 170 W = 14.47, i.e. 15 sections of the radiator.
Manufacturers strive to indicate excessive heat transfer indicators of their products, assuming that the temperature of the coolant in the system will be maximum. In real conditions, this requirement is rarely observed, so you should focus on the minimum heat transfer indicators of one section, which are reflected in the product passport. This will make the calculations more realistic and accurate.
If the room is non-standard
Unfortunately, not every apartment can be considered standard.This applies even more to private residential buildings. How to make calculations taking into account individual operating conditions? For this you will need to consider many different factors.

When calculating the number of heating sections, it is necessary to take into account the height of the ceiling, the number and size of windows, the presence of wall insulation, etc.
The peculiarity of this method is that when calculating the required amount of heat, a number of coefficients are used that take into account the characteristics of a particular room, which can affect its ability to store or give off thermal energy.
The formula for the calculations is as follows:
CT = 100 W / sq. m * P * K1 * K2 * K3 * K4 * K5 * K6 * K7where
CT - the amount of heat required for a particular room;
P - room area, sq. m;
K1 - coefficient taking into account the glazing of window openings:
- for windows with ordinary double glazing - 1.27;
- for double-glazed windows - 1.0;
- for windows with triple glazing - 0.85.
K2 - coefficient of thermal insulation of walls:
- low degree of thermal insulation - 1.27;
- good thermal insulation (laying in two bricks or a layer of insulation) - 1.0;
- high degree of thermal insulation - 0.85.
K3 - the ratio of the area of windows and floor in the room:
- 50% — 1,2;
- 40% — 1,1;
- 30% — 1,0;
- 20% — 0,9;
- 10% — 0,8.
K4 - coefficient allowing to take into account the average air temperature in the coldest week of the year:
- for -35 degrees - 1.5;
- for -25 degrees - 1.3;
- for -20 degrees - 1.1;
- for -15 degrees - 0.9;
- for -10 degrees - 0.7.
K5 - adjusts the need for heat taking into account the number of external walls:
- one wall - 1.1;
- two walls - 1.2;
- three walls - 1.3;
- four walls - 1.4.
K6 - accounting for the type of room that is located above:
- cold attic - 1.0;
- heated attic - 0.9;
- heated living space - 0.8
K7 - coefficient taking into account the height of the ceilings:
- at 2.5 m - 1.0;
- at 3.0 m - 1.05;
- at 3.5 m - 1.1;
- at 4.0 m - 1.15;
- at 4.5 m - 1.2.
It remains to divide the result by the heat transfer value of one section of the radiator and round the result to an integer.
When installing new heating radiators, you can focus on how effective the old heating system was. If her work suited you, it means that the heat transfer was optimal - these data should be based on in the calculations. First of all, it is necessary to find on the Web the value of the thermal efficiency of one section of the radiator, which must be replaced. Multiplying the found value by the number of cells that made up the used battery, one obtains data on the amount of thermal energy, which was enough for a comfortable stay. It is enough to divide the result by the heat transfer of the new section (this information is indicated in the technical passport for the product), and you will receive accurate information about how many cells will be needed to install the radiator with the same indicators of thermal efficiency. If earlier the heating could not cope with the heating of the room, or vice versa, it was necessary to open the windows due to constant heat, then the heat transfer of the new radiator is adjusted by adding or decreasing the number of sections.
For example, earlier you had a common cast-iron battery MC-140 of 8 sections, which pleased with its heat, but did not suit the aesthetic side. Paying tribute to fashion, you decided to replace it with a branded bimetallic radiator assembled from separate sections with a heat transfer of 200 W each. The nameplate power of a spent heat appliance is 160 watts, however, over time, deposits appeared on its walls that reduce heat transfer by 10-15%. Consequently, the real heat transfer of one section of the old radiator is about 140 watts, and its total thermal power is 140 * 8 = 1120 watts. Divide this number by the heat transfer of one bimetallic cell and get the number of sections of the new radiator: 1120/200 = 5.6 pcs.As you can see for yourselves, in order to keep the heat transfer of the system at the same level, a bimetallic radiator of 6 sections will be sufficient.
How to consider effective power
When determining the parameters of the heating system or its individual circuit, one of the most important parameters, namely the thermal pressure, should not be discounted. It often happens that the calculations are performed correctly, and the boiler heats well, but somehow it does not add to the heat in the house. One of the reasons for the decrease in thermal efficiency may be the temperature regime of the coolant. The thing is that most manufacturers indicate the power value for a pressure of 60 ° C, which takes place in high-temperature systems with a coolant temperature of 80-90 ° C. In practice, it often turns out that the temperature in the heating circuits is in the range of 40-70 ° C, which means that the temperature head does not rise above 30-50 ° C. For this reason, the heat transfer values obtained in the previous sections should be multiplied by the actual pressure, and then the resulting number should be divided by the value indicated by the manufacturer in the data sheet. Of course, the figure obtained as a result of these calculations will be lower than that obtained by calculation using the above formulas.
It remains to calculate the actual temperature head. It can be found in the tables on the expanses of the Network, or calculated independently by the formula ΔT = ½ x (Tn + Tk) - Tv). In it Tn is the initial temperature of the water at the entrance to the battery, Tk is the final temperature of the water at the outlet of the radiator, and Tv is the temperature of the external environment. If we substitute in this formula the values Тн = 90 ° С (the high-temperature heating system mentioned above), Тк = 70 ° С and Тв = 20 ° С (room temperature), then it is easy to understand why the manufacturer focuses on this particular temperature head . Substituting these numbers in the formula for ΔT, we just get the "standard" value of 60 ° C.
Given not the passport, but the real power of the thermal equipment, it is possible to calculate the system parameters with an allowable error. All that remains to be done is to amend 10-15% for the case of abnormally low temperatures and provide for the possibility of manual or automatic adjustment in the design of the heating system. In the first case, experts recommend putting ball valves on the bypass and the coolant supply branch to the radiator, and in the second, install thermostatic heads on the radiators. They will allow you to set the most comfortable temperature in each room, without releasing heat to the street.
How to adjust the calculation results
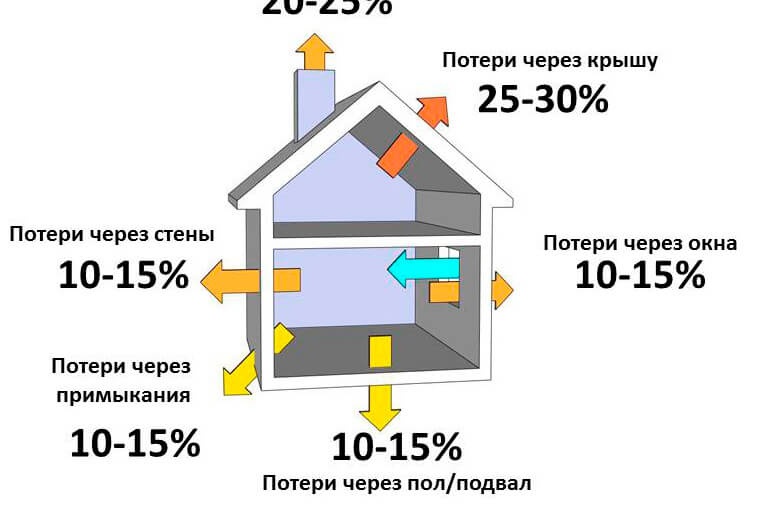
When calculating the number of sections, it is necessary to take into account the heat loss. In the house, heat can go in a rather significant amount through walls and adjacencies, floor and basement, windows, roofing, natural ventilation system.
And you can save if you insulate the slopes of windows and doors or a loggia by removing 1-2 sections, heated towel rails and a stove in the kitchen also allow you to remove one section of the radiator. Using a fireplace and underfloor heating, proper insulation of walls and floors will minimize heat loss and will also reduce the size of the battery.
The number of sections may vary depending on the operating mode of the heating system, as well as on the location of the batteries and the connection of the system to the heating circuit.
In private houses, autonomous heating is used, this system is more efficient than centralized, which is used in apartment buildings.
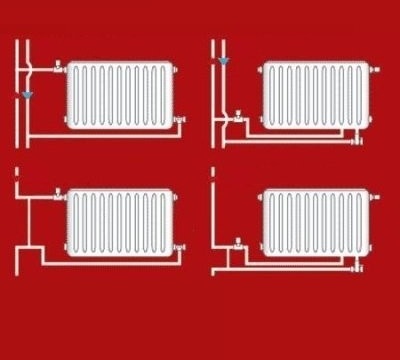
The way radiators are connected also affects heat transfer performance. The diagonal method, when water is supplied from above, is considered the most economical, and the lateral connection creates a loss of 22%.
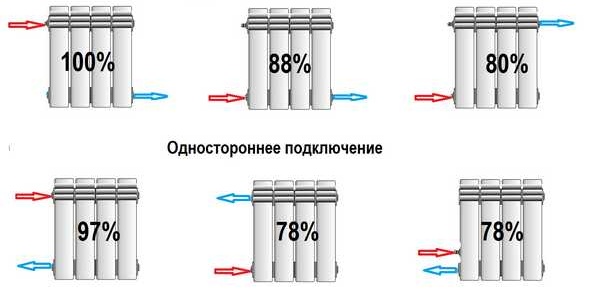
The number of sections may depend on the mode of the heating system and the way radiators are connected
For single pipe systems, the end result is also subject to correction.If two-pipe radiators receive a coolant of the same temperature, then the one-pipe system works differently, and each subsequent section receives cooled water. In this case, first make a calculation for the two-pipe system, and with the top increase the number of sections, taking into account heat losses.
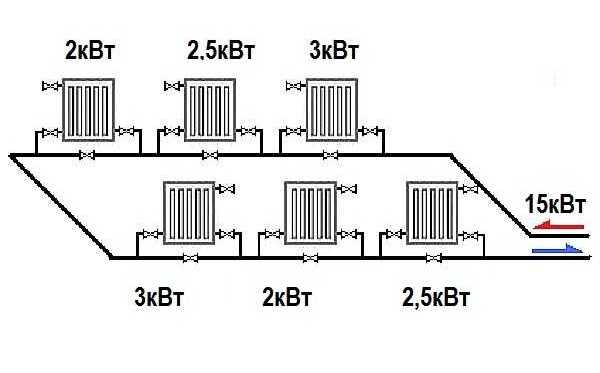
The calculation scheme for a single-pipe heating system is presented below.
If we have 15 kW at the input, then 12 kW remains at the output, which means 3 kW is lost.
For a room with six batteries, the losses will average about 20%, which will create the need to add two sections to the battery. The last battery with such a calculation should be of enormous size, to solve the problem, installation of shutoff valves and connection via bypass are used to regulate heat transfer.
Some manufacturers offer an easier way to get an answer. On their sites you can find a convenient calculator specifically designed to make these calculations. To use the program, you need to enter the necessary values in the appropriate fields, after which the exact result will be displayed. Or you can use a special program.
Such a calculation of the number of heating radiators includes almost all the nuances and is based on a fairly accurate determination of the room’s heat demand.
Adjustments allow you to save on the purchase of extra sections and pay bills for heating, provide for many years economical and efficient operation of the heating system, and also allow you to create a comfortable and cozy atmosphere of heat in the house or apartment.
Material updated 02/05/2019


5 comments