Water distribution in an apartment - comparison of tee and collector circuits

Starting repairs, we are rarely limited to one room. The updated interior begins to discord with the rest of the rooms, and somehow not only new wallpapers, the color of the floor and ceiling, but also furniture in other rooms beg themselves. And if it comes to overhaul, then he will touch on everything and everything: electrical wiring, soundproofing, heating and air conditioning, even the water distribution in the apartment. As you know, water supply is a system of technical devices (fittings, valves, filters) and pipes for supplying water to different points of the apartment. The water distribution can be performed in the classic tee way or modern collector.
Classics of the genre - tee wiring diagram
The tee layout of the water distribution in the apartment is a consecutive connection of pipes from the common riser to the places of water consumption (taps, shower, toilet, dishwasher or washing machine).
First, the main pipes with hot and cold water are discharged, and then branches are made from them using tees.
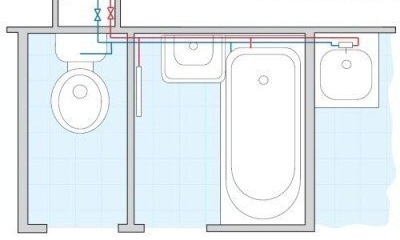
The tee pattern is the cheapest option. When designing the wiring, the plumber should talk about it, and the collector circuit, as well as the cost of both options
Advantages of the classic scheme:
- low cost;
- compactness;
- ease of installation.
The disadvantages of this wiring system:
- pressure drops caused by the simultaneous inclusion of two points of water consumption;
- it is impossible to block one consumer; you have to turn off the water in the entire apartment;
- it is not always possible to conveniently place tees in the bathroom area.
In some cases, you can avoid a complete shutdown of the water during the repair work. To do this, put a faucet in front of the plumbing, which can be closed if necessary.
The tee scheme is more suitable for a small apartment in which it is easy to coordinate water consumption at different points. But such a water distribution in a private house can cause a lot of inconvenience, especially in large cottages. The collector circuit is more convenient for them.
The collector circuit is ideal for a large house
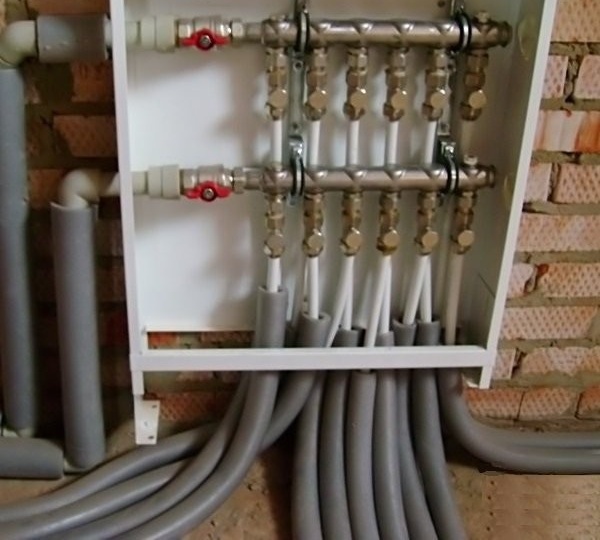
Collector wiring of a water supply system involves bringing individual pipes to each point of water consumption. Sink in the kitchen, toilet, shower - each faucet in the house delivers the right amount of water regardless of the others. Pipes are supplied from a collector installed at the water inlet to the house. It is a device having one input and several conclusions. Their number is selected based on the number of points of water consumption. At the same time, you need to consider not only taps, but also a washing machine and dishwasher, water on the street, etc.
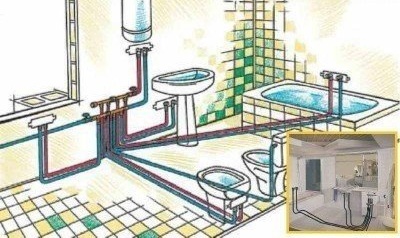
Here it is clearly seen that all points of water consumption are independent of each other. It is very convenient during operation and repair.
The collector can only be installed after water filters and pressure reducers are connected.

This is how the collector looks under the sink. Agree, it’s not very convenient for an ordinary apartment. Something even resembles an airplane dashboard
This scheme has many advantages. Firstly, without harming households, you can turn off the water in the shower, while leaving the possibility of using other bathrooms.
Secondly, all the taps for controlling the water supply system are located in one place and are easily accessible. As a rule, the collector is located in a sanitary cabinet or in a separate room.
Thirdly, stable pressure in the system. Collector wiring protects against drops, thereby ensuring that you don’t get boiling water in your soul if someone turns on the water in the kitchen.
Fourth, the minimum risk of breakdowns and ease of repair, because from the tap to the manifold there is only one solid pipe.

In a private house, when using the collector scheme, water pipes can be hidden even under the screed: the probability of breaking whole pipes is negligible
Fifthly, the water temperature at all points of water consumption is the same, even if you open all the taps at the same time.
Sixthly, the connection of new taps or equipment that uses water, is carried out quickly, without prejudice to other consumers. To do this, you only need to install a collector with a margin of several conclusions.
Everything has its drawbacks, and the collector method is no exception. It requires a large amount of building materials. Two pipes here are not enough. And this, in turn, leads to significant material costs. And the installation of a water supply system according to this scheme takes a lot of time.
In addition, a lot of space is needed to accommodate the manifold and such a number of pipes. You can’t hide the place where the water supply entrance into the apartment behind the cabinet; it does not look aesthetically pleasing.
Which water pipes to choose depending on the wiring diagram
If in the apartment the distribution of water pipes will be performed according to the tee scheme, then it is better to use plastic or polypropylene pipes.
Plastic pipe connections are made using special welding. Threaded metal joints are mounted in polypropylene fittings (connection details).

Polypropylene pipes are the most affordable on the market. They are lightweight and last about thirty years.
As sealants, sanitary flax, paste or FUM tape are used. The latter is a sealing PTFE material.
For wiring by the collector method, it is necessary to use metal-plastic water pipes.
They are designed to work under high pressure, easy to bend, and cut with ordinary precision scissors. Collet fittings are suitable for their connection.
Copper pipes are not subject to corrosion, have unique bactericidal properties.

Copper pipes are an elite option. Long-life, wear-resistant, with bactericidal properties. But ordinary buyers are repelled by a high price
They serve much longer than any other - from fifty to one hundred years. However, they are rarely chosen because of the very high cost.
In addition to the correct choice of pipes and connections for performing water distribution, it is necessary to protect the pipes from external factors. Corrosion, heat loss, stray currents, condensate, abrasive friction and mechanical damage - each of them can lead, at best, to repair and additional costs.



