How to calculate various parameters of pipes: basic formulas and calculation examples

Water, heating, sewer, chimney, casing, copper, steel, plastic, metal-plastic, narrow, wide pipes for various purposes from various materials surround us everywhere. The need to build new communications or replace old ones arises both during the construction of the house and during the current repair. When preparing a project for the upcoming work, it will not hurt to arm yourself with a calculator to calculate the weight of the pipe, its mass, volume and other parameters.
Content
Why do you need to calculate pipe parameters?
A preliminary calculation of the parameters of the pipes is necessary in many cases. For example, for proper communication of the pipeline with other elements of the system. Designers and installers when working with pipes use indicators such as:
- patency of the pipeline;
- heat loss;
- amount of insulation;
- amount of material to protect against corrosion;
- roughness of the inner surface of the pipe, etc.
As a result, you can determine the exact number of pipes required for a particular system, as well as their optimal characteristics. Correct calculations save you from excessive costs for the purchase and transportation of material, allow substances that are in the pipeline to move at a given speed for the most efficient use of the system.
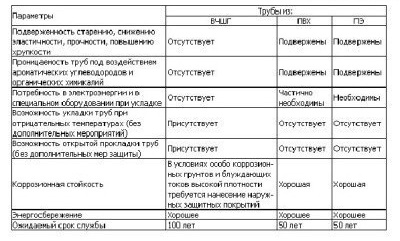
This table provides some useful information about the characteristics of different types of pipes, which will help you choose the right structures needed to create the pipeline
In heating systems, the diameter of the pipes substantially depends on the permissible speed. An example of this kind of calculation is presented in the video:
Calculations of various pipe parameters
In order to correctly calculate the main parameters of the pipes, the following indicators should be determined:
- material of which the pipe is made;
- type of pipe section;
- inner and outer diameter;
- Wall thickness;
- pipe length, etc.
Part of the data can be obtained simply by measuring the design. A lot of useful information is contained in certification documents, as well as in various reference books and state standard specifications.
How to know the diameter and volume of the pipe?
Some calculation formulas are familiar to every student. For example, if you need to clarify the diameter of a particular pipe, you should measure its circumference. To do this, you can use a centimeter tape, which is used by seamstresses. Or you should wrap the pipe with another suitable tape, and then measure the resulting segment with a ruler.
Next, use the formula for the circumference:
L = πD, where:
- L is the circumference of the circle;
- π is a constant number "pi" equal to about 3.14;
- D is the diameter of the circle circle.
It is enough to do a simple transformation to calculate the external diameter of the pipe using this formula:
D = L / π.
By measuring the wall thickness of the pipe, it is also easy to calculate the inner diameter of the circle. To do this, double the value of the pipe wall thickness from the value of the outer diameter of the pipe.
Calculation of the cross section of the pipe
To calculate the cross section of the pipe, calculate the area of the circle. This takes into account the difference between the outer diameter of the pipe and the thickness of its walls, in other words, the inner diameter of the pipe.

This figure clearly shows such indicators as the outer diameter of the pipe and the thickness of its wall. The difference between the outer diameter and thickness allows you to calculate the inner diameter of the pipe
The circle area formula looks like this:
S = πR², where:
- S is the area of the circle;
- π is the number of "pi";
- R is the radius of the circle, calculated as half the diameter.
If you use information about the outer diameter and wall thickness of the pipe, the formula may look like this:
S = π (D / 2-T) ², where:
- S is the cross-sectional area;
- π is the number of "pi";
- D is the outer diameter of the pipe;
- T is the wall thickness of the pipe.
Suppose there is a pipe whose outer diameter is 1 meter and the wall thickness is 10 mm. First you need to agree on all units. The wall thickness will be 0.01 meters. According to the above formula, we calculate the cross section of such a pipe:
S = 3.14X (1m / 2-0.01m) ² = 0.75m²
Thus, the cross section of the pipe with the specified parameters will be equal to 0.75 square meters. m
As you know, the accuracy of calculations with the number "pi" depends on the number of decimal places that are used when applying this constant. However, construction usually does not need ultra-precise calculations, and the number of pi is assumed to be 3.14. The final result also makes sense to round up to two decimal places.
How to calculate pipe volume?
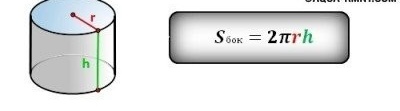
This diagram illustrates the use of data such as the radius of the pipe section and its length to determine the volume of the pipe
To calculate the volume of a specific pipe segment is also not difficult. To do this, you first need to find the circumference of the pipe by its outer diameter according to the formula above:
S = π (D / 2) ² or S = πR²
In this case, D is the outer diameter of the pipe, and R is the outer radius, i.e. half the diameter. After this, the obtained value must be multiplied by the length of the pipe segment, having received the volume, which is expressed in cubic meters. The formula for calculating the volume of the pipe may look like this:
V = SH, where
- V is the volume of the pipe, cubic m
- S - external cross-sectional area, sq.m .;
- H is the length of the pipe segment, m
Suppose there is a pipe with an external diameter of 50 cm and a length of 2 meters. All units must be agreed first. D = 50 cm = 0.5 m. Substitute this value in the circle area formula:
S = π (D / 2) ² = 3.14 (0.5 / 2) ² = 0.0625 m²
Now you can calculate the volume:
V = SH = 0.0625X2 = 0.125 m³.
All these calculations can be easily done using a conventional calculator, but it is much more convenient to use the appropriate computer that performs the calculation online.
The calculator performs calculations depending on the initial data: pbase radius and height, base diameter and height, or base area and height.
How to calculate the weight of the pipe?
Information on the weight of a specific number of pipes is necessary in order to predict the cost of their transportation. If a large structure is used, its weight does not hurt to correlate with the bearing capacity of the foundation of knowledge.
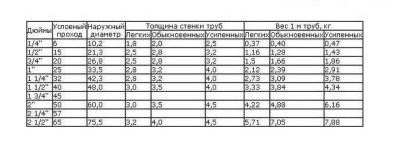
This table shows reference data on the weight of steel pipes of various types, taking into account their sizes and features of the production technology
Middle school students are well aware that the mass of an object can be found by multiplying its volume by the density of the substance of which this object consists. Builders are relieved of the tedious calculations of the mass of a particular pipe segment, since various construction directories contain information about the weight of a running meter of the most various types of pipes.The easiest way is to calculate the mass of the pipe using the relevant GOSTs, using information on:
- the material of which the pipe is made;
- its outer diameter;
- wall thickness;
- inner diameter, etc.
Having found out the weight of one running meter of the pipe, multiply the obtained value by the total number of running meters. The complexity of the task corresponds to the level of the fourth to fifth grade of a comprehensive school.
To find out the weight of the pipes, we suggest you use our online calculator. Enter the necessary information in the appropriate fields, after which the program displays the weight value of the specified number of pipes.
How to determine the outer surface of the pipe?
When installing a wide variety of systems, piping insulation may be required. In order to determine as accurately as possible the required amount of heat-insulating material or other necessary coating (anticorrosion, waterproofing, etc.), it is recommended to calculate the area of the outer surface of the pipe.

In order to correctly calculate the amount of material required for pipe insulation, calculate the area of its outer surface. To do this, the circumference of the outer section should be multiplied by the length of the pipe
Any pipe of circular cross section can be imagined as a rectangle that has been rolled up into a tube. The area of a rectangle is defined as the product of its length and width. In the case of a pipe, the length of the rectangle will correspond to the length of the pipe, and its width to the length of its outer circumference.
The circle length formula was already mentioned at the beginning, it looks like L = ∏D. Denote the length of the pipe segment as H. Then the outer surface area of the pipe will be equal to:
St = πDH, where:
- St - the area of the outer surface of the pipe, sq.m .;
- π is a constant number pi equal to 3.14;
- D is the outer diameter of the pipe, m;
- H - pipe length, m
For example, if there is a pipe with a diameter of 30 cm and a length of 5 meters, its surface area will be equal to:
St = πDH = 3.14X0.3X5 = 4.71 sq.m.
Using the above formulas, it is possible to easily calculate the volume of the inner space of the pipe and the area of its inner surface. To do this, in the calculations it is enough to replace the value of the outer diameter of the pipe by the value of its inner diameter.
And if the pipe section is not round?
All formulas and calculations described earlier consider exclusively pipes with a circular cross section. Indeed, in modern construction these structures are most often used. However, there are pipelines with:
- rectangular;
- oval;
- trapezoidal section, etc.
To calculate such non-standard pipes, it is recommended to use a number of simple formulas. So, the area of a square or rectangular section is defined as the product of length and width. Multiplying the area by the length of the pipe segment, you can calculate the volume of the pipe. To find the surface area of a pipe of rectangular cross section, multiply the length of the pipe segment and the perimeter of the section. The perimeter, as you know, is the sum of all sides of the rectangle.

Pipes with a rectangular or trapezoidal section are most often used to create chimneys and sewer systems. To calculate the main parameters of such pipes, several simple formulas are used
The trapezoid perimeter is also calculated as the sum of all its sides. We multiply this data by the length of the pipe segment and get the surface area of the pipe. To calculate the volume of a pipe with a trapezoidal cross-section, you must first find the area of the trapezoid.It is calculated as the product of half the sum of its bases and height:
S = 0.5 (A + B) H, where:
- A and B - the length of the bases of the trapezoid, i.e., its parallel sides;
- H is the height of the trapezoid, i.e., a perpendicular drawn from one base to another.
Multiplying the area of the trapezoidal section by the length of the pipe segment, we obtain its volume.
To calculate the parameters of a pipe with an oval cross section, they act in approximately the same way. The circumference of the oval, as well as its area, is calculated. Multiplying the circumference by the length of the pipe segment, we obtain the surface of the pipe. The product of the oval cross-sectional area and the length of the pipe segment gives the value of the pipe volume.
The oval has two axes: large and small. The circumference of the oval (or ellipse) is calculated as the product of the number "pi" by the sum of the lengths of its semiaxes:
L = πX (A + B), where:
- ∏ is a constant number pi equal to 3.14;
- A and B are the length of the semi-axes of the oval.
The oval area is calculated as the product of its semiaxes and the number "pi":
S = πAB.
To avoid complex calculations, you can use numerous online calculators that allow you to calculate the parameters of pipes of various configurations.


