Fiberglass pipes: how are they manufactured, where are they used, labeling + performance

In the laying of communications (water supply, sewer networks), the role of the conductor is played by pipes. Even a couple of decades ago, metal products dominated in this segment, because there were simply no other options. Meanwhile, Europe has been working with fiberglass pipes for more than 60 years, giving them preference for anticorrosion “impenetrability”. With us, they "take root" slowly due to the high price. But if you look at the novelty in a comprehensive manner, then servicing such pipelines will cost less than repairing and replacing rusted metal. Let's try to figure out how good fiberglass pipes are and where they are used.
For all its unknown to the ordinary consumer, fiberglass pipelines were laid in the military sphere even under the USSR. But because of the secrecy inherent in the defense sphere, information about them, of course, did not spread. And import from foreign countries was prohibited. That is why information about pipes made of glass composite material began to leak out only by the 80's. of the last century, although America has been releasing them since 1944
Fiberglass is referred to as composites exhibiting extraordinary strength at low density. It includes fiberglass with binders (epoxy resins or PEFs).
Types of pipes for a binder additive
Pipes differ in those additives that bind all components (fiberglass, quartz sand) into one solid material. These include epoxy and polyester resins. All manufacturers of fiberglass pipes choose one of the additives, taking into account the manufacturing technology and future use of the product.
Pipes with PEFs
Polyester resins are used more often than epoxides. After passing through all stages of processing, a pipe with such an additive becomes invulnerable both for acids, salts, alkalis, and for corrosion, therefore, it can be used in many sectors of construction (especially fiberglass pipes of large diameter).

Fiberglass pipes of large diameter are in demand in the laying of treatment facilities, because they do not accumulate sludge on the inner walls
With their help, they lay:
- pipelines with cold water;
- sewer networks;
- engineering systems at hydroelectric power stations;
- molting;
- land reclamation and irrigation facilities;
- drainage systems;
- treatment facilities;
- wells;
- water intakes.
But fiberglass at PEF is afraid of temperatures above 90 degrees and pressures above 32 atmospheres, so for such critical working conditions, pipes on epoxy are used.

When creating fiberglass pipes, the main raw materials are fiberglass, quartz sand and binders (resins)
Epoxy Pipes
Epoxy gives glass-fiber pipes the ability to withstand pressure up to 240 atmospheres and temperatures up to 130 degrees.Their thermal conductivity is so low that the outer wall is not thermally insulated, because this is not necessary.
Fiberglass pipes, which will be used in industry, are most often created on epoxy resin. In the conditions of private housing construction, such high-strength material can be used only in the heating system and hot water supply.
Industrial applications:
- Oil industry (at any stage of oil production or transportation).
- Chemical industry (for laying pipelines through which aggressive substances are transported - acids, salts, etc.).
- Housing and utilities (in heating and hot water).
- Energy industry (in pipelines, cooling thermal power plants, and in desalination plants).
Glass composite material on PEFs costs less than epoxy because the feedstock is cheaper. In addition, such increased strength is not needed in conventional piping systems through which cold water is supplied to homes or sewage is discharged.

The strength and resistance of fiberglass to chemical agents allows the use of pipes in the oil and gas industry
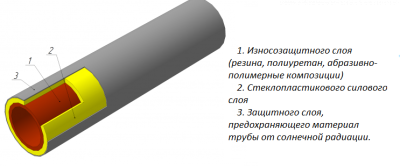
The structural features of this type of pipe
The modern production of fiberglass pipes uses two technologies (continuous winding and centrifugal molding). Taking into account the planned use, pipes with one, two and three layers are produced. Each layer adds strength and resistance to external factors.
So, single-layer structures have only one, the main (aka structural) layer, consisting of fiberglass and the additives listed above.
Two-layer reinforce external protective layer, the main function of which is to resist the aggression of substances in the soil or ultraviolet rays during surface mounting.
In three-layer pipes there is a power layer located between the protective and structural. It increases the strength of the pipe, eliminates the difference in external and internal pressure and temperature.
Multilayer products are used only in specific industries.
Symbols and markings
Fiberglass pipes are distinguished by a protective inner coating, each of which is indicated by its marking.
- n - pipes for drinking water supply, through which cold water will go.
- g - for hot water supply.
- and - for pipelines through which liquids with abrasive particles will flow.
- x - for systems with chemically active substances.
- s - for other needs.
Fiberglass pipes have a number of undeniable advantages:
- The term of non-repairable use is about fifty years.
- 4 times lighter than steel.
- Installation is much cheaper (does not require welding) and can be carried out regardless of the weather.
- Not subject to corrosion.
- Do not deposit sediment inside the pipe.
- Withstand high temperatures and high pressure.
The use of fiberglass pipes in private housing construction is not yet very common, but the industry has managed to assess the convenience of the new material. During the repair of existing pipelines, many enterprises began to replace metal with fiberglass.