All about the expansion tank for heating: why is it needed, how does it work and how to choose one?

The physical properties of any coolant practically do not allow this fluid to compress. An attempt to even slightly reduce the volume immediately leads to a sharp jump in pressure. Water, when heated in the range from 20 to 90 ° C, expands. These two properties explain the need to allocate space in the system for the "breathing" of the coolant. An expansion tank for heating must ensure the safe and reliable operation of all components of the engineering system. The duration of its operation directly depends on whether this element was correctly selected and installed.
Content
Types of expansion tanks and their comparison
Different types of expansion tanks can be installed in the heating system.
Open expansion tanks
An open expansion tank is an open tank into which you can always add coolant. It does not require shutoff valves, a rubber membrane and even a cover. Usually a bucket through it is “added” to the system liquid, although a water tap can always be taken out of the water supply.
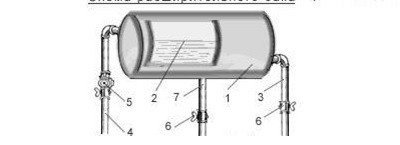
The operation scheme of the open expansion tank: 1 - tank body; 2 - coolant level; 3 - cold pipe; 4 - downpipe; 5 - safety valve; 6 - shutoff valve; 7 - the highest point in the riser of the heating system pipe
A few decades ago, open structures were widely used that compensated for the change in the volume of the coolant during natural circulation. However, constant monitoring of the liquid level and its “topping up”, installation difficulties at the top point, low pressure and metal corrosion - all this led to the coming to the fore of closed systems and tanks.
Enclosed expansion tanks
Where the coolant circulates the pump, they install closed tanks, popularly referred to as "diaphragms." It is always painted red and is structurally a sealed container, inside of which is installed a membrane made of technical rubber. But in the blue tanks, designed to organize hot water supply, less durable food rubber is used.
The device of the expansion tank is as follows: a membrane in the form of a cylinder or diaphragm divides the tank into two parts. Inert gas or air is pumped into the upper one, and the other is diverted for excess coolant.
With increasing temperature, the excess expanding coolant enters the tank. The volume of the air chamber decreases, and the pressure in the chamber with air increases, which just compensates for the high pressure in the system. With a decrease in the temperature of the coolant, the reverse process is observed.
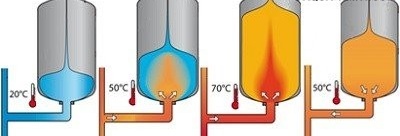
At low coolant temperature, the tank is empty, and the membrane occupies the maximum possible volume. When heated, the liquid begins to fill the cavity between the membrane and the container. Cooling down, the coolant is compressed, and air begins to “push” it back into the system
The closed expansion tank of the heating system can be equipped with a flange (replaceable) or non-replaceable membrane. The only, but significant advantage of the latter type is its low cost. The membrane is rigidly fixed around the perimeter of the tank. In the initial position, it is pressed to the inner surface, as the whole volume is filled with gas. If coolant enters the expansion tank, the pressure increases.
When the system starts, there is a risk of rupture of the diaphragm, as the pressure rises sharply. In the future, the readings on the pressure gauge change smoothly and do not pose a threat to its integrity.
In order to prevent damage to the membrane, in large-volume heating systems, the pressure is monitored using a pressure gauge. The safety valve is activated when the maximum permissible value is reached. Usually it ranges from three and a half to four bars for private homes.
A flange expansion tank has several advantages:
- the maximum pressure is much greater than that of a tank with a non-replaceable diaphragm;
- the ability to replace the membrane through the flange in case of damage or rupture;
- vertical and horizontal execution of products. This gives more accommodation options in a small boiler room.
Which is better - open or closed?
If we compare the operational and consumer properties of open and closed types, the following facts prove the advantage of the latter:
- a closed tank is not carried up, therefore, it is possible to save on pipes;
- membrane tanks have smaller overall dimensions;
- the coolant from the closed tank will not exactly evaporate;
- minimal heat loss, in contrast to the open tank requiring additional insulation;
- protection of pipes and system components from corrosion, which is ensured by the lack of air;
- a closed heating system can operate at high pressure, while an open heating only at low;
- diaphragm operating costs lower than that of an open tank.
But in general, of course - you choose.
Before buying an expansion tank for heating, you need to perform the appropriate calculations and design the system. Read more about this in our material:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/voprosy/kak-rasschitat-rasshiritelniy-bak.html.
.
Tank position in the heating system
The expansion tank of the heating system serves to compensate for the increase in the volume of the coolant as a result of its thermal expansion.
If forced circulation, then the pressure at the connection point of the unit is equal to the static pressure at this point at a given temperature (the rule only applies if there is one diaphragm). If we assume that it will change, it turns out that in a closed system a certain amount of liquid appeared from nowhere. This is contrary to common sense.
An open heating system is a vessel that has a complex shape with specific convection flows. All nodes should provide a quick rise of the hot coolant to the upper point and its subsequent gravity drain through radiators into the boiler. In addition, the design of the system should not impede the movement of air bubbles up.
In this case, the expansion tank is always located at the highest point of the one-pipe system, usually at the top of the booster manifold.
Calculation of the volume of the expansion tank heating
There are several ways to determine the volume of the expansion tank. Firstly, numerous design offices and individual specialists offer their services.They use special software for calculations, which allows you to take into account all the factors affecting the stable operation of the heating system. This is all, of course, wonderful, but expensive.
Secondly, it is possible to independently calculate the expansion tank according to the formulas. Here you need to be especially careful, since the slightest mistake can significantly distort the final values. Everything is taken into account: the volume of the heating system, the type of coolant and its physical characteristics, pressure.
Thirdly, you can use on-line calculators to perform calculations. True, in this case, it is better to double-check the results on several resources in order to exclude the possibility of incorrect page operation.
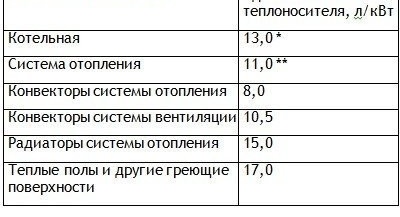
Fourth, you can estimate by eye - the specific capacity of the heating system is equal to 15 l / kW. These are indicative figures. This method is suitable only at the stage of a feasibility study. Immediately before the purchase, more accurate calculations are necessarily carried out.
Method # 1 - calculation by formulas
The basic formula for the calculation is as follows:
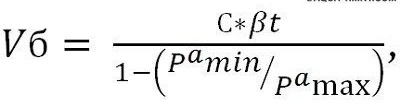
where C is the total volume of coolant in the heating system, l;
Pa min - adjusting (initial) absolute pressure in the expansion tank, bar;
Pa max - maximum (limit) absolute pressure, which is possible in the expansion tank, bar.
When calculating the total volume of the heating system, all pipes and radiators, underfloor heating and the boiler, as well as other elements, are taken into account. Approximate values are shown in the table:
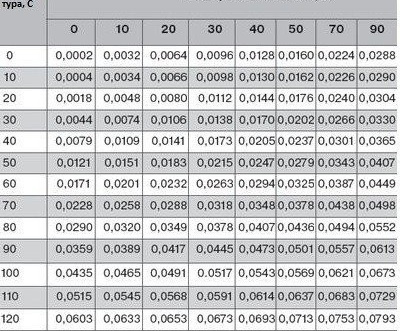
The table shows the values of the coefficient βt - an indicator of the thermal expansion of the coolant, which correspond to the maximum temperature difference in the working and non-working systems.
Now we calculate Pa min and Pa max according to the formulas:

The first formula calculates the absolute adjustment pressure (h2 is substituted with a minus sign when the tank is located below the insertion point). The second formula determines the absolute maximum possible pressure in the expansion tank.
Method # 2 - online calculator for calculating
To calculate the volume of the expansion tank, you can use the on-line calculator. There are many of them.
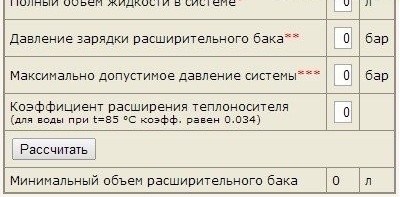
* - it is better to take the most accurate figure. If there is no data, then 1 kW of power is equal to 15 l;
** - must equal the static pressure of the heating system (0.5 bar = 5 m);
*** - this is the pressure at which the safety valve is activated.
This technique is greatly simplified and suitable only for the calculation of individual heating systems. Step by step we will analyze the scheme using a specific example:
- we determine the type of coolant: in this case it is water. The coefficient of its thermal expansion is 0.034 at a temperature of 85C;
- we calculate the volume of coolant in the system. For example, for a 40 kW boiler, the water volume will be 600 liters (15 liters per 1 kW of power). It is possible, and this will be a more accurate figure, to summarize the volume of coolant in the boiler, pipes and radiators (if such data is available);
- the maximum allowable pressure in the system is set by the threshold value at which the safety valve is activated;
- the charging pressure (initial) of the expansion tank can be greater than or equal to (but in no case less) the hydrostatic pressure of the heating system at the point of insertion of the diaphragm;
- expansion volume (V) is calculated by the formula V = (C * βt) / (1- (Pmin / Pmax));
- round the estimated volume up (this will not affect the system in any way).
The expansion tank is selected so as to compensate for this calculated volume (see table):
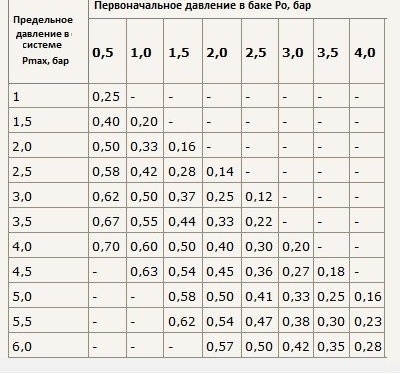
The coolant filling factor of the expansion tank is determined according to the table based on a combination of the maximum and initial pressure values. Further, the calculated volume is multiplied by a coefficient and the resulting figure is the recommended volume of the membrane
Membrane expansion tanks can be used when installing a closed heating system. Read about it in our next article:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/otoplenie/razvodka-otopitelnoj-sistemy/zakrytaya-sistema-otopleniya.html.
Last few tips
An important criterion for choosing an expansion tank is the setting of the safety valve (safety valve), which is an obligatory element for the expansion unit (SP 41-101-95 "Design of heating points"). The threshold value after which the protection is triggered is 10% higher than the acceptable for the "weakest link" of the system (such settings take into account the difference in the height of the membrane and valve).
To be able to control the maximum permissible pressure in the system, give preference to valves with the ability to adjust. A mandatory requirement for all such protective devices is the presence of a “detonation” device (forced opening). It allows you to periodically check the operability of the valve and prevent sticking of the valve.
The selection of the expansion tank is carried out taking into account the quality, resistance to diffusion and operational characteristics of the membrane (diaphragm), the range of operating temperatures, and the service life. Be sure to make sure that the threshold pressure values in the boiler and tank match, and also check that the diaphragm meets the safety and quality requirements for such units.



3 comments