Leningradka heating system: design rules and implementation options

Customized construction is becoming increasingly popular. Despite the economic instability, people prefer to independently solve the problems of gaining housing. Practice shows that in the end it will turn out faster and cheaper. The question of how to make a house warm with minimal heating costs and simple installation is very relevant among homeowners. The Leningradka heating system, simple in design, meets these requirements as well as possible: it is quite efficient and economical, and it is easy to install and maintain. Another valuable quality of such heating is an independent connection, which abstracts the “Leningrad” from central heating.
Before proceeding with installation
Depending on the architectural solutions inside the building and the heating method, such a system can be performed in horizontal and vertical versions. This issue is resolved at the preliminary design stage.
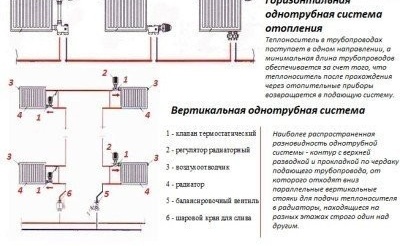
Before proceeding with the calculations, it is necessary to decide which type is preferable - vertical or horizontal
Also at the design stage, they are determined with the type of coolant: it can be water or household antifreeze. Non-freezing liquid (non-freezing) is pre-diluted with water, based on the calculated data of special temperature tables.
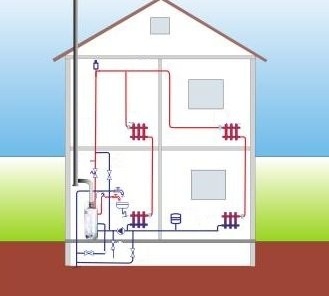
It should be borne in mind that in most cases, heating occurs using the natural circulation of the coolant: the heated fluid moves through pipes and radiators, giving them the heat received during heating.
Please note: the effective operation of the vertical system with the natural movement of the coolant will only be with its length not exceeding 30 m.
Read about our choice of coolants for different heating systems in our review article:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/otoplenie/radiatory/teplonositel-dlya-sistem-otopleniya.html.
How does such a system work?
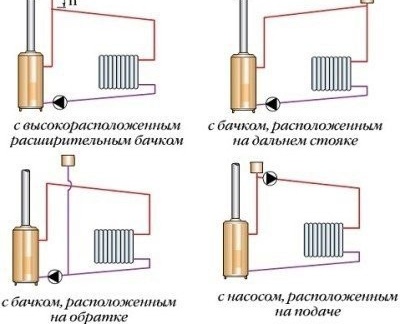
The principle of operation of the heat supply circuit as a whole can be represented as a system that includes a heating source (boiler), a damper (expansion tank), heating batteries with Mayevsky cranes, supply pipelines and "return". A simple “Leningradka” heating scheme involves heating the coolant in the boiler and moving it through the supply pipe. At regular intervals, heating radiators are connected, through which the coolant passes. Having passed the last heating device, the cooled liquid is sent back to the boiler along the return line. It turns out a closed loop.
Attention! System capacity is limited. Water heating is accompanied by an increase in internal hydraulic pressure, which can lead to a rupture of the system and damage to its elements. That is why the Leningradka must necessarily have an expansion tank at its highest point.An open damper removes air from the system and balances the pressure in it.
Device sequence
- A single-pipe heating system “Leningradka” is mounted as follows:
- A vertical pipe with a damper mounted on it crashes into the supply pipe immediately near the boiler.
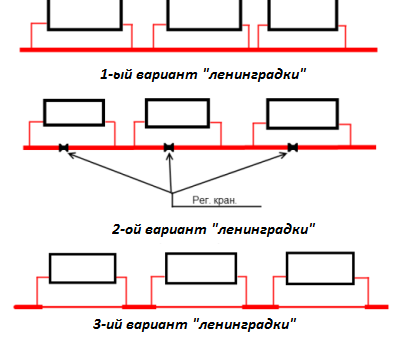
- Throughout the main highway, radiators or radiators are connected by means of a tie-in. Either a bottom connection or a full bore (diagonal) can be made. The first option makes it possible to uniformly warm the entire area of the radiators, especially if they are 12-section. Avoiding “stagnant” zones is possible by constantly heating the fluid in motion.
- In order to turn off individual heaters in non-visited rooms in order to save heat energy or during repair work, additional shut-off and distribution valves are installed: regulators, thermostat valves, valves, etc.
Important: “Leningradka” makes it possible to selectively transfer heat to each radiator.
In case of inefficiency of natural circulation, as well as for raising the coolant to a high height, pressure hydraulic devices (pumps) are used, in which case the circulation becomes forced.
You will learn how to choose a circulation pump, what types are from our next material:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/otoplenie/documents/cirkulyacionnyi-nasos-dlya-otopleniya.html.
Some features of vertical installation
Vertical private house heating system "Leningradka" involves raising the coolant to a great height, usually with a pump. With this arrangement of elements, the heat exchangers warm evenly and faster, even with pipes of a small working section. But even without injection equipment, the heat exchange process occurs due to the movement of flows of different temperature: the warm layer, rising up, displaces the colder back to the boiler.
Note: in the absence of a pump, pipes of larger diameter (but not metal) should be installed in order to reduce the resistance to movement of the coolant, as well as provide the required slope.
The desire to create a single-tube heating system in private housing is due to the availability of the acquisition of all its elements, simple installation, preventive maintenance and repair. The main thing is that everything is correctly calculated and to be sure of the effectiveness of such heating.