Natural circulation heating system: device rules + analysis of typical schemes
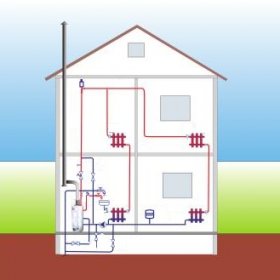
No matter how engineers and builders predicted in the eighties, the heating system with natural circulation lives and lives in the twenty-first century, and it also heats our homes. Pumping equipment significantly increases the cost of the boiler and makes it dependent on the mains, so many refuse it. The gravity system is the cheapest and easiest in design. Of course, it has its drawbacks, the main of which is the restriction on the area of the building. Due to the low inertia, it is suitable for houses up to a hundred square meters.
Content
How does the principle of natural circulation work?
The coolant, most often it is ordinary water, moves along the contours from the boiler to the radiators and vice versa due to a change in its thermodynamic characteristics. When, when heated, the density of the liquid decreases and the volume increases, it is squeezed out by a cold stream going to their return, and rises through the pipes. As the coolant is distributed by gravity along the horizontal branches, the temperature drops and it returns to the boiler. So the cycle closes.
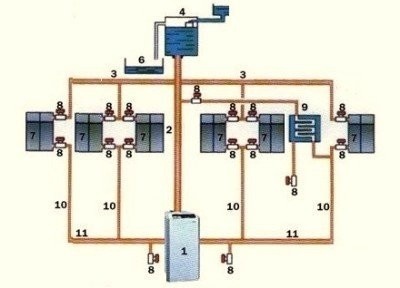
Diagram of a heating system with natural circulation: 1 - solid fuel boiler, 2 - main riser, 3 - distributing pipes, 4 - expansion tank, 5 - water tank to replenish the expander, 6 - pipe that removes excess coolant into the sewer (capacity), 7 - heat exchangers, 8 - ball valves, 9 - boiler, 10 - return, 11 - reverse riser
If water heating with natural circulation was chosen for the house, then all horizontal sections of pipes are laid with a slope that goes along the direction of the liquid. This allows you to effectively deal with "airing»Batteries. Air is lighter than water, so it rushes up through the pipes, enters the expansion tank, and then, accordingly, into the atmosphere.
The tank receives water, the volume of which increases with increasing temperature, and creates a constant pressure.
What determines the circulation pressure?
The creation of the desired circulation pressure must be calculated when designing a heating system. It depends on how the levels of the middle of the boiler and the lowest radiator differ. The greater the elevation difference, the better the fluid moves through the system. It is also affected by the density difference between hot and cooled water.
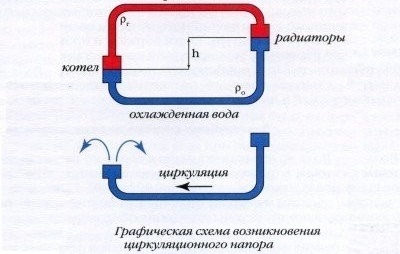
The circulation pressure in the heating system, first of all, depends on the difference in the height of the boiler and the lower radiator.The larger this difference (h), the greater the pressure
Heating with natural circulation is characterized by a cyclical change in temperature in the heat exchangers and in the boiler, which occurs along the central axis of the devices. Hot water is at the top, cold water is at the bottom. Under the influence of gravity, the cooled coolant moves down the pipes.
The circulation pressure directly depends on the height of the batteries. Its increase is also facilitated by the angle of inclination of the supply line, directed towards the radiators, and the slope of the return pipe facing the boiler. This allows the coolant to more easily overcome the local resistance of the pipes.
When installing a heating system with natural circulation in a private house, the boiler is installed at the lowest point so that all radiators are higher.
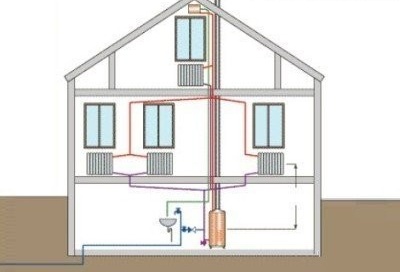
In the cottage, when installing a heating system with natural circulation, the boiler is installed at the lowest point. All heat exchangers (radiators) must be higher
For apartment buildings, heating circuits with natural circulation are used very rarely, since when installing in an apartment, the boiler is lowered into the “hole” - directly onto the floor slab. The floor around it is cut out, and the recess and the perimeter around it should be protected by fireproof materials.
Schemes of such heating systems
The scheme of the heating system, regardless of the way the coolant circulates, depends on several factors:
- a method for connecting radiators to supply risers. Single tube and double tube systems are distinguished here;
- places for laying a hot water supply line. You need to choose between the lower and upper wiring;
- highway laying schemes: deadlock system or associated coolant movement in the highways;
- the location of the risers, which can be either horizontal or vertical.
Monotube system: how to regulate temperature?
Single pipe heating system It has only one wiring option - the top one. There is no return riser in it, so the coolant cooled in the batteries returns to the supply line. The movement of the liquid is provided by the difference in temperature of the liquid in the lower and upper radiators.
To ensure the same temperature in the rooms on different floors, the surface of the heating devices on the first floor should be slightly larger than on the second and subsequent ones. A mixture of hot and chilled water in the upper heat exchangers enters the lower radiators.
In a single pipe system there can be two options for movement coolant: in the first one part goes to the radiator, the other - further down the riser to the lower appliances.
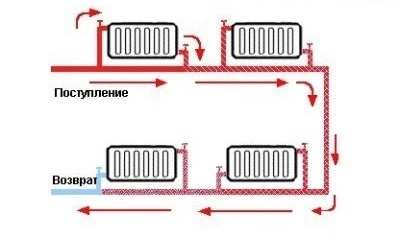
With parallel single-pipe wiring, the heat exchangers on the upper floors receive hot water, and the lower ones get cooled. Therefore, the area of the latter should be increased in order to equalize the heating of all rooms
In the second case, the entire volume of water passes through each heat exchanger, starting with the uppermost ones. The main feature of this wiring is that the radiators on the first and basement receive only chilled water.
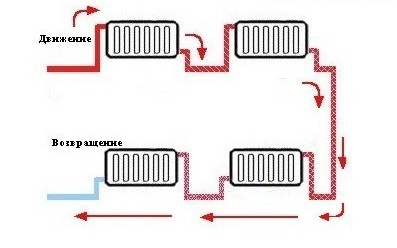
With a flow-through version of a single-pipe wiring, you cannot turn off or limit the flow of coolant to a separate radiator. Overlapping one of them would stop circulation in the entire system
And if in the first case it is possible to regulate the temperature in the rooms with the help of taps, then in the second they cannot be used, as this will lead to a decrease in the liquid supply to all subsequent heat exchangers. In addition, a complete shut-off of the tap would mean stopping the circulation of water in the system.
When installing a one-pipe system, it is better to stop at the wiring, which makes it possible to adjust the water supply to each radiator. This will allow you to adjust the temperature in individual rooms and, of course, makes the heating system more flexible, and therefore more efficient.
Since a single-pipe wiring can only be top, its installation is possible only in buildings with an attic. This is where the feed pipe should be located. The main disadvantage is that the start of heating is possible only throughout the building at once. The system also has advantages, of course. The main ones are simple installation and lower cost. In terms of aesthetics, the smaller the pipes, the easier it is to hide them.
How should a two-pipe system be arranged?
This version of the heating scheme assumes the presence of a supply and outlet line. Hot coolant circulates in the upper part of the system, and cooled in the lower part.
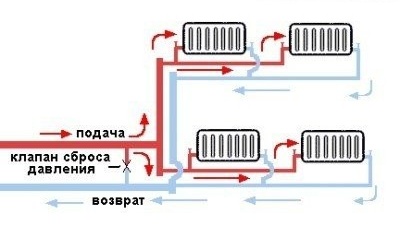
The two-pipe heating system is more flexible with regard to temperature control in individual rooms. However, it requires more materials than single pipe
A pipe is connected from the boiler connected to the expansion tank. From the tank there is a pipe of the hot line of the circuit, which then connects to the wiring. Depending on the size of the tank and the volume of water in the system, an overflow pipe may leave the tank. On it, excess water is discharged into the sewer.
Pipes exiting the bottom of the heat exchangers are combined into a return line. On it, the cooled coolant again enters the boiler. The return must go through the same rooms as the supply pipe.
Horizontal or vertical riser wiring?
The heating system with a vertical riser involves connecting radiators to it from different floors. Its advantage: lower risk of "airing" of the system, the disadvantage is a higher cost.
When heat exchangers from one floor are connected to the supply pipe, this is a horizontal riser system. This option will cost homeowners a smaller amount, but will have to solve the problem of air congestion. As a rule, it is enough to install air vents.
Pros and cons of arranging this type of heating
As for the advantages of a heating system with natural water circulation, there are several of them:
- lack of difficulties during installation, commissioning and operation;
- thermal stability of the system. Based on the gravitational circulation of the coolant, it provides maximum heat transfer and maintains the microclimate in the premises at a given level;
- profitability (with proper insulation of the building);
- quiet work. No pump - no noise and vibration;
- independence from power outages. Naturally, in the case when the installed boiler can work without electricity;
- long term of operation. With timely maintenance without major repairs, the system can work for 35 years or more.
The main disadvantage of the gravitational heating system is the restrictions on the area of the building and the radius of action. It is installed in houses, the area of which usually does not exceed 100 square meters. Due to the small circulation pressure, the radius of the system is limited to thirty meters horizontally. A mandatory requirement is the presence of an attic in the building in which the expansion tank will be installed.
A significant disadvantage is the slow warming up of the whole house. With a system with natural circulation, it is necessary to insulate the pipes passing in unheated rooms, since there is a risk of freezing water.
Usually, a little material is used for such wiring, but when the local resistance of the pipeline needs to be reduced, costs increase due to the need for larger pipes.


1 comment