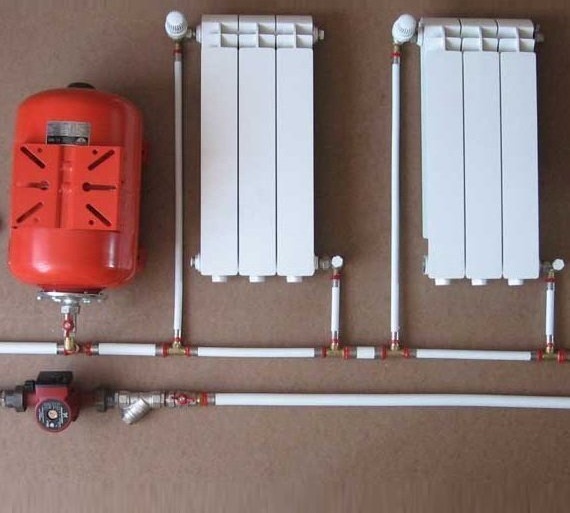
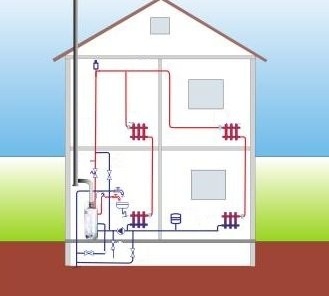
Features of the device and examples of heating circuits with pump circulation
Arrangement of the heating system is a responsible and rather difficult task. There are many varieties of construction. It is considered to be the most affordable structure with natural circulation, which does not require the installation of additional equipment. However, in order to minimize the main drawback of such a design, low circulation pressure, it will be necessary to install pipes with a large diameter. Which leads to problems with the choice of radiators and increases the cost of the pipeline. Thus, heating systems with pump circulation turn out to be more practical, which can work with any types of radiators and pipelines of a small diameter of greater length.
Content
General concepts
As the name implies, the hallmark of the system is the presence circulation pumpproviding advancement of the heat carrier. Water heated to the required temperature is sent through a supply pipe to a heating device using a pump. Cooling down, it enters the boiler along the return pipes. In addition, an expansion tank is necessarily present in the system, which helps to create stable pressure and accepts the volume of coolant that increases with heating.
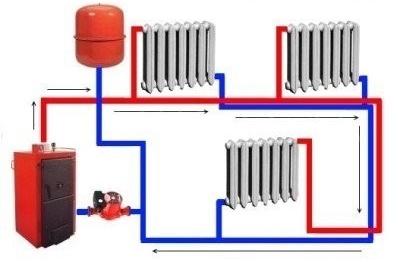
The built-in pump moves the coolant through the pipelines, thereby ensuring optimal pressure and maximum effect of using the system
The circulation and expansion pipes from the tank must enter the return line in front of the pump. In this case, the distance between the connection sections is at least 2 m. The bottom of the expansion tank is positioned at least 800 mm above the highest point of the structure. To make air easier to be removed from the system, it is necessary to ensure the associated movement of the coolant. To do this, the supply line is laid with the lift towards the distant riser, and flowing air collectors are mounted on the highest sections.
On the bases of the risers, gland plug valves are usually installed, providing the ability to disconnect them from the system. At the inlet sections of the heating devices, control valves are installed. The speed of the coolant in the pipes has certain limitations, otherwise noise will be heard during the functioning of the heating. So for residential premises this value is 1.5, 1.2 and 1 m / s with pipeline diameters of 10, 15 and 20 mm.
There are several varieties of the system. They are divided into:
- By the location of the risers on the structure with horizontal and vertical risers.
- For installation of the supply line for options with lower and upper wiring.
- By the method of connecting heating devices to two-pipe and single-pipe.
- According to the scheme of the highway to devices with associated movement of the coolant and dead ends.
You can read more about choosing a coolant for a heating system in our next article:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/otoplenie/radiatory/teplonositel-dlya-sistem-otopleniya.html.
Let's consider all options in more detail.
Horizontal and vertical riser?
The horizontal system involves connecting radiators to one riser, which is best placed outside the living area: in the corridor or on the stairwell. The main advantage of this option is saving pipes and lower installation costs. The disadvantages include some difficulties in operation and a tendency to education air congestion in system. For their bleeding on radiators, Majewski taps are usually installed. A horizontal structure is used most often in single-storey buildings of a large area.
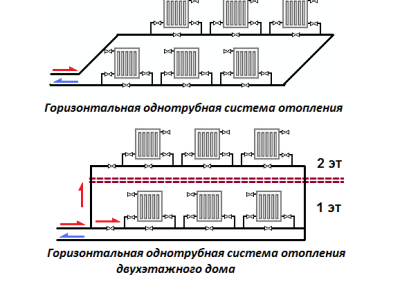
The horizontal arrangement of the system allows you to save on pipes and installation. However, such a system has a tendency to airing, which requires the installation of additional equipment, for example, Mayevsky cranes
When arranging a vertical system, all heating devices are brought to a vertical riser. This method allows you to individually connect each floor of a multi-storey building. The main advantage - during operation, air jams are not formed. However, arranging a vertical version of the system will cost slightly more than the horizontal.
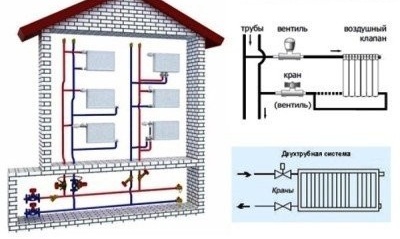
The vertical design is not prone to the appearance of air jams during operation, but more expensive in the arrangement
Lower or upper wiring?
The device with the lower wiring is mounted so that the inlet and outlet pipes are installed below the radiators. The system provides a slight slope to deal with air traffic jams. For the same purpose, the design is equipped with Mayevsky cranes. A certain advantage that the lower wiring gives is the introduction of heating into operation in stages, as the floors are erected. What can be very relevant for individual construction.

Designs with lower wiring suggest placing the boiler and highways below the level of radiators, which allows the gradual commissioning of the heating system
The upper wiring involves placing the supply pipe above the heating appliances. Most often it is mounted in the attic or in the inter-ceiling space. The coolant rises up and from there it is distributed throughout the premises. In this case, the return pipe is always installed below the radiator. At the highest point of the structure, an expansion tank is mounted, which performs its functions and is responsible for eliminating the possibility of air jams. The system is not acceptable for buildings with flat roofs.
The basic principles of designing a heating wiring with diagrams are presented in the following material:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/otoplenie/razvodka-otopitelnoj-sistemy/sxema-otopleniya-v-chastnom-dome.html
Single pipe versus double pipe
The main distinguishing feature of the single-tube design is one pipe to which the heater is connected. Radiators are connected in series. The coolant cools in each of them and is suitable for subsequent devices with a lower temperature. Thus, the last in the battery chain is much colder than the first. The advantage of the system is the relatively low cost of components and installation. However, there are significant disadvantages.
The first is the inability to regulate the temperature of the radiators. You can neither reduce nor increase the heat transfer, nor can you disconnect the battery from the system. However, when installing devices using a special jumper, called bypass, it will be possible to turn off the radiator if necessary. But indirect heating of the room with the help of feed pipes and riser will continue.
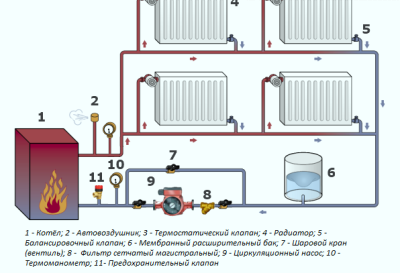
A single-pipe heating system does not imply the possibility of regulating the temperature of the coolant in the radiators, in addition, less hot water enters each subsequent heater in the chain
The second significant drawback is the temperature difference of the heaters connected in series. To level it as much as possible, you can choose radiators different sizes. In this case, the smallest should be the first, and the area of all subsequent gradually increases. However, the appearance of the rooms in which the system will be located may suffer from such a variety.
Double pipe systems suggest supply and outlet pipes to each radiator. Thus, the coolant coolant in the equipment is discharged into the boiler, and does not enter the next device. This allows water to be supplied to the radiators at approximately the same temperature. The system is free from the disadvantages of single-tube structures. It can use pipes with a smaller diameter and connections of smaller sizes, which makes the design more aesthetic and allows you to use it with a hidden installation, for example, in a screed for the floor.
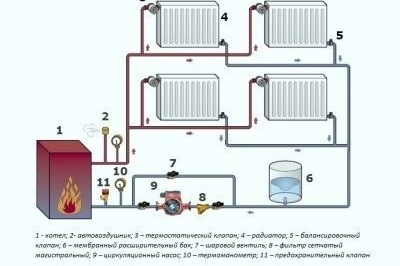
A distinctive feature of the two-pipe system: the inlet and outlet lines are suitable for each radiator, which allows maintaining the same coolant temperature on the way to all devices
Parallel connection of two-pipe radiators is very convenient. When installed on each device, a crane is installed, which makes it possible to adjust the temperature of the equipment. If necessary, it can be used to disconnect the battery from the system and replace or repair it. There are models of thermostatic regulators that allow you to adjust the temperature in the room automatically. The main disadvantage of two-pipe structures is a larger number pipesnecessary for arrangement. This makes the system more expensive and more difficult to install.
Deadlock and associated schemes
Dead-end designs suggest that the movement of the cooled coolant in the return line will be opposite to the direction of the heated in the flow. In such a system, the length of the circulation rings is different. For appliances located at the largest distance from the boiler, the maximum length of the circulation ring. As the equipment location approaches the boiler, the length of the circulation ring decreases. Therefore, it is quite difficult to achieve uniform heating of all heating appliances. Those that are closer to the main riser will always warm up better.
Another challenge: precise alignment of the circulation rings. Especially in the case when the load on the closest to the main riser is small. However, despite all the shortcomings, deadlock systems are among the most economical. To level their “minuses” in practice they reduce the total length of highways and mount several small structures instead of one long one. Thus, it is possible to achieve the possibility of good horizontal adjustment of the system.
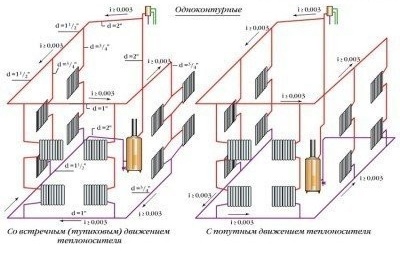
Deadlock systems are distinguished by different lengths of circulation rings, whereas in a system with an accompanying motion of the coolant they are the same
In some cases, the heating system has enough natural circulation. About how it is arranged, what is the principle of work, read in our material:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/otoplenie/razvodka-otopitelnoj-sistemy/sistema-otopleniya-s-estestvennoj-cirkulyaciej.html
Devices with passing movement are distinguished by the same length of the circulation rings. Due to this, all heating devices operate in exactly the same conditions, which gives equal heating of all batteries, regardless of their removal from the main riser. Moreover, such systems are used to a limited extent, since their arrangement requires more pipes than for a dead-end design.Most often, they are installed in cases where the linking of the circulation rings within the limits recommended by SNiP is impossible.
Pump circulation heating is more practical and efficient. The pump, built into the design, provides the optimal speed of the fluid in the pipes, which allows you to get the maximum possible effect from the use of the heating system. A variety of arrangement options makes it possible to choose the optimal design for your conditions, which will provide the most comfortable conditions in a heated building.