Classifications of steel pipes and fittings + an overview of the rules for working with them

A pipeline is an integral part of most engineering structures, be it a heating system, sewage system or water supply system. Not so long ago, a steel pipe was actively used to equip all these communications. However, with the advent of plastic parts that are not susceptible to corrosion and ease of installation, they began to use it much less often. New technologies make it possible to produce modernized steel products that are less susceptible to corrosion. The presence of special fittings allows you to mount pipelines of various configurations without the use of welding. All this has significantly increased the demand for steel parts, the variety of which we will understand.
Content
Assortment of steel products
Steel pipes are a general term that unites an extensive group of products. There are several classifications of parts.

The cross section of steel pipes can be of very different shapes. In addition to traditional round products, rectangular, six and octagonal, oval, square and other elements can be found on sale.
Types of pipes by linear dimensions
Based on this feature, several types of elements are distinguished:
- According to the outer diameter, all pipes are divided into products of medium diameter (102-426 mm), small diameter (5-102 mm) and capillary (0.3-4.8 mm).
- According to the geometry of the section, square, oval, round, segment, ribbed, octagonal and hexagonal, rectangular parts, etc. are distinguished.
- Based on the ratio of the outer diameter to the width of the wall, especially thin-walled, thin-walled, normal, thick-walled and especially thick-walled products are produced.
- By processing class. The first class involves trimming the edges of the pipe and deburring. The second class is only cutting parts.
- Elements vary in length, which is short, measured and unmeasured.
Types of products by production method
All steel products can be produced in one of two ways: using welding or without it. Accordingly, the details can be both with a welded seam, and without it. In the first case, the steel sheet is folded in various ways, after which it is welded in an inert gas by tungsten electrodes. This is the so-called TIG welding. Alternatively, a high frequency current welding method or HF welding is used.
The steel tape can either be rolled up into a tube, then a straight seam is obtained, or it is wound in a spiral, as a result of which spiral-shaped products are obtained. Water and gas pressure and profile pipes are produced only by the welded method.

Steel pipes can be made using welding or without it.Profile and water-pressure pipes always have a seam
Seamless parts are made of steel rods by drilling, cold or hot deformation and casting. In the first case, the steel cylinder is drilled; in the latter, the molten metal is poured into the mold inside which the rod is mounted. However, deformation methods are most often used for production. In the hot method, the rod is heated in a furnace to a plastic state and sent to the rollers, where it is brought to the required length and diameter.
Cold deformation implies that before processing in the rollers, the workpiece cools, but it is annealed before the start of the final calibration. In this way, thick-walled pipes are produced. Based on the production method, the assortment of steel pipes is as follows. Electric welded are divided into:
- helical;
- straight-seam;
- profile;
- water and gas pressure.
Accordingly, seamless are divided into cold-formed and hot-formed.
Classification by type of anti-corrosion coating
Corrosion protection can be carried out in various ways. For these purposes, various coatings are used: extruded polyethylene, cement-sand mixture, polyethylene laid in one, two or three layers, epoxy-bitumen mixture or zinc. In the latter case, cold or hot dip galvanizing is used.
Advantages and disadvantages of steel parts
Steel pipes have many advantages:
- Wide range of operating temperatures. The metal loses its strength characteristics at temperatures above 500 °, so the pipe can withstand 100 ° and even 200 ° without any problems. Moreover, in this mode, the pipeline can be operated for years.
- Availability of material. Standard products from structural steel, as well as pipes made of stainless steel, can be purchased almost everywhere.
- High strength and resistance to longitudinal and lateral loads. The maximum pressure for steel pipelines can be measured in tens of atmospheres. The stern fittings and pipes are extremely difficult to damage.
The steel pipeline is very strong and reliable, but it is not without drawbacks. So the steel parts warm up very quickly. This is very good for heating systems and bad for transporting liquid and gas media, which should be carried out in a stabilized temperature mode. In the latter case, the carrier cools quite quickly, the pipe cools even faster. At low temperatures, the part may burst, unable to cope with the expansion of the cooling fluid. To prevent this, steel pipes are usually protected by heating systems or cover with insulation.
Also, without protection, the steel is covered with a thin layer of rust after a few hours of operation. It is not scary for its strength, but the quality of the transported water is deteriorating. It can not be used as drinking, in addition, there is an increased risk of the formation of silty deposits, which are easily superimposed on loose rust. Product performance is irreversibly deteriorating. Special protection is required to prevent these unpleasant phenomena.

Steel pipes have insufficient corrosion resistance. After a few hours of operation, the internal walls of the product are covered with a layer of rust
Initially, steel pipes were connected only by welding. This is the most complex and time-consuming installation option. Today he has alternatives: thread assembly or collet. These are simpler methods, but even they require the performers to have at least the minimum knowledge and skills of plumbing. In addition, the products are massive, which complicates an already difficult installation.
Types and classification of fittings
Fittings are used to assemble pipelines of various configurations.They are reliable, structurally simple and do not create additional problems in operation. On sale you can find parts that allow you to work with pipes of various diameters: from 16 to 110 mm. It must be remembered that:
- Elements with a diameter of 16 to 63 mm can only be used for systems with a maximum pressure of 16 atm.
- Parts ranging in size from 75 to 110 mm are designed for structures whose maximum pressure does not exceed 10 atm.
Fittings, if necessary, allow you to connect parts made of different materials, but with the same thread, as well as designs with different diameters.

Several types of fittings for steel pipes are available. Among them crosses, tees, couplings and other details
The purpose of the connecting elements for steel pipes is indicated in the marking of the parts. There are several types of fittings:
- Crosses. Designed for branching four pipes. They are distinguished by the presence of four outputs located at an angle to each other. Most often they are located at right angles to each other.
- Squares. Used to change the direction of the highway in the horizontal or vertical plane. The slope angle varies from 45 ° to 90 °.
- Tees. The part is similar to a cross, but has only three exits. Models are produced for parts with equivalent, as well as for products with different diameters.
- Couplings. Connecting elements intended for installation of straight sections of highways. Products are produced with equivalent outputs, as well as with nozzles varying in diameter.
There are two classifications of parts. One of them is based on the dimensions of the pipes and involves dividing the product range into many sizes. The second involves the allocation of several types according to the method of installation of connecting elements.
Fittings for welding
A distinctive feature of such elements is the presence of at least one “clean” end, on which there is no thread, or any other fasteners. It is intended for applying a weld. To fix an element, the following operations are performed:
- Parts are stacked on the welding table and precisely aligned. Then they are “caught” by two point seams.
- The fitting aligns with the central axis of the pipe. For this, a special device is used - the caliber.
- The groove between the pipe and fitting is filled with a weld, which is performed by moving the electrode along the joint line.
Read more about welding in other articles on our website.

Fittings designed for mounting under welding have at least one smooth end that will be fixed to the pipe by welding
Threaded elements
Such fittings are distinguished by the presence of an internal thread, the diameter and standard pitch of which is determined according to special GOST. Installation of parts is carried out in stages:
- The end part of the pipe is equipped with a thread. The procedure can be performed in two ways: either weld a threaded fitting, or simply cut the desired number of turns.
- Then you should pick a lock nut of the right size and wind the element onto the pipe bend.
- Sgon is wrapped with FUM polymer sealing tape, after which the fitting is screwed onto it.
- The joint is tightened with a lock nut.
The use of threaded elements is the best way to arrange a detachable connection. If you intend to transport aggressive liquids, it is better to choose fittings made of stainless steel.

The use of threaded fittings is the best way to arrange a detachable connection on a section of a steel pipeline
Crimp fittings
These are products similar to crimp elements for plastic piping. Details are used to equip a collapsible connection of sections of the highway with an external diameter of less than 60 mm. Product installation is carried out as follows:
- Installation begins with the dismantling of the fitting.The clamping nut is unscrewed and the clamping ring, seal and washer are removed from the housing.
- The pipe is measured, after which it is cut at an angle of 90 °. The bevel is necessarily removed from the end.
- The sealant is installed in the body of the product. A clamping nut, ring and washer are put on the pipe.
- By precise movement, the pipe is pressed into the fitting. In this case, it passes through the seal, which is tightened by a nut.
- The collet ring moves to the fixation area, and the whole system is firmly fixed with a clamping nut. It presses on the ring, ensuring the tightness of the connection.
Installation of the pipeline using crimp fittings can be considered the most simple and fastest option. However, the high strength of such a compound cannot be guaranteed.
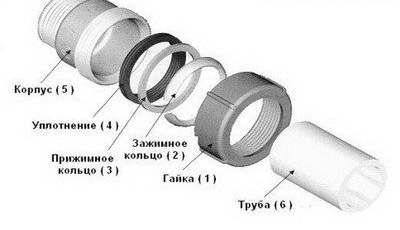
Crimp fittings for steel pipes are similar in design to the elements used for plastic products. It must be understood that the connection made with their help is notable for its low strength.
Steel pipes are an excellent solution for arranging communications. Not so long ago they were considered unpopular. However, today part of their inherent disadvantages are successfully leveled. Modern products are protected against corrosion. In addition, they can be connected using a variety of fittings, which greatly simplifies and speeds up the installation process. Thus, using steel products, it is quite easy to equip a reliable and durable pipeline that will function smoothly for many years.


