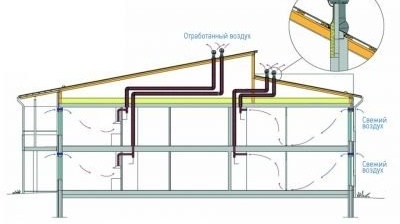
The principle of operation, arrangement and installation of the natural ventilation system

There is no doubt about the need for ventilation in the house. The appearance of mold on the walls and corners, increased humidity in the room (and this is additional stuffiness in the summer and cold in the winter) - all this is a consequence of stagnant air saturated with vapors of human activity. Over time, the fungus Discula brunneotingens settles on the walls, and a person has to breathe its spores, forming colonies in wooden floors, frames and doors. The result is a decrease in immunity, allergic diseases and bronchial asthma, decreased psychological tone and chronic fatigue syndrome. But there is a solution to the problem, and not one.
Content
The principle of operation and natural ventilation in a private house
Ventilation is a set of measures and devices that ensures the maintenance of a continuous exchange of air in residential and office buildings. The following types of ventilation are distinguished:
- Artificial and natural. The first assumes the availability of special devices, the second - their absence
- Exhaust and supply. Separation occurs depending on the direction of movement of the air mass. Exhaust involves air removal, supply - forcing into the premises.
- General and local. This characteristic describes the range of ventilation.
- Channelless and channel. Classification is based on the presence (or absence) of air ducts.
- Permanent and periodic. Permanent ventilation operates automatically, non-stop. Periodic occurs from time to time, it includes the opening of doors, windows and windows.
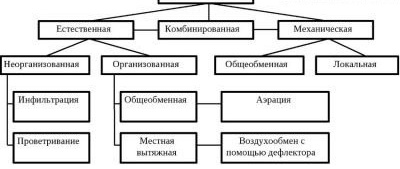
In addition to natural ventilation, you can arrange artificial (mechanical) or combine these two types in a combined version
In houses with many premises for various purposes, as a rule, combined ventilation options are used. When considering each species individually, both advantages and disadvantages are found. In order to choose the best option, you must carefully familiarize yourself with all possible types of ventilation.
The easiest and oldest way to ventilate rooms is natural ventilation.
Not only people know about ventilation, but also bears - plunging into hibernation, they leave a small hole at the top of the den for the influx of fresh air.
The principle of natural ventilation is based on the known laws of aerodynamics.
Two physical parameters - temperature and pressure - control the flow of air masses from one place to another.
- Air moves from the high pressure zone to the low zone.
- Warm air always tends up, cold air down.
- The greater the pressure or temperature difference, the faster the air moves.
Knowing these simple patterns allows you to control ventilation in a house or apartment. If air masses move under the influence of natural factors, such ventilation is considered spontaneous. If the movement is due to special holes made in the walls, then such air exchange is called organized. Organized natural ventilation, in addition, is divided into:
- gravitational;
- longline;
- aeration.
For most homes and apartments, natural ventilation is sufficient. Of course, provided that it is organized correctly and competently. Approximate and accurate calculations allow optimal use of ventilation ducts, save time and materials, choose the right places for installing air passages and air vents.
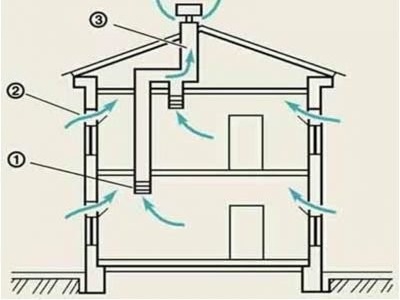
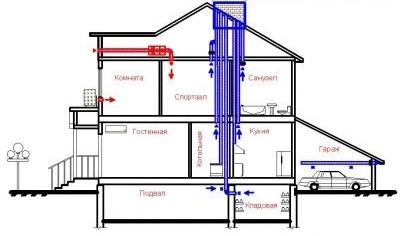
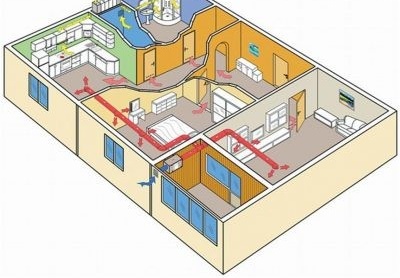
Air flows in the natural ventilation circuit enter through special openings (2), pass through the rooms and are removed through the ventilation pipe (1) to the main ventilation shaft (3)
Calculation of ventilation and ventilation duct cross-section (taking into account the volume of the room)
Since supplying people with air in residential and industrial premises is a vital function, ventilation is calculated in accordance with regulatory documents. These include:
- SNB 4.02.01–03 - sanitary safety standards from the Ministry of Health;
- SP 60.13330.2012 - a set of rules arising from applicable Federal laws and State Standards;
- SNiP 41–01–2003 - building codes from the Ministry of Construction.
Details can be found on official departmental sites.
An accurate calculation of all ventilation parameters can only be done by an experienced specialist. There are a large number of formulas and calculation tables that take into account the various nuances of the movement of air masses, such as:
- total area of the room;
- the purpose of the room as a whole and its individual components;
- the height of the premises;
- the presence and number of exhaust ducts;
- height of ventilation ducts;
- functional purpose of ventilation.
Table: air flow in ducts for designing ventilation systems
| Duct Parameters | Air Consumption (m³ / h) at air speed: |
||||||
| Diameter round duct |
Dimensions rectangular duct |
Area sections duct |
2 m / s | 3 m / s | 4 m / s | 5 m / s | 6 m / s |
| 80 × 90 mm | 72 cm² | 52 | 78 | 104 | 130 | 156 | |
| Ø 100 mm | 63 × 125 mm | 79 cm² | 57 | 85 | 113 | 142 | 170 |
| 63 × 140 mm | 88 cm² | 63 | 95 | 127 | 159 | 190 | |
| Ø 110 mm | 90 × 100 mm | 90 cm² | 65 | 97 | 130 | 162 | 194 |
| 80 × 140 mm | 112 cm² | 81 | 121 | 161 | 202 | 242 | |
| Ø 125 mm | 100 × 125 mm | 125 cm² | 90 | 135 | 180 | 225 | 270 |
| 100 × 140 mm | 140 cm² | 101 | 151 | 202 | 252 | 302 | |
| Ø 140 mm | 125 × 125 mm | 156 cm² | 112 | 169 | 225 | 281 | 337 |
| 90 × 200 mm | 180 cm² | 130 | 194 | 259 | 324 | 389 | |
| Ø 160 mm | 100 × 200 mm | 200 cm² | 144 | 216 | 288 | 360 | 432 |
| 90 × 250 mm | 225 cm² | 162 | 243 | 324 | 405 | 486 | |
| Ø 180 mm | 160 × 160 mm | 256 cm² | 184 | 276 | 369 | 461 | 553 |
| 90 × 315 mm | 283 cm² | 204 | 306 | 408 | 510 | 612 | |
| Ø 200 mm | 100 × 315 mm | 315 cm² | 227 | 340 | 454 | 567 | 680 |
| 100 × 355 mm | 355 cm² | 256 | 383 | 511 | 639 | 767 | |
| Ø 225 mm | 160 × 250 mm | 400 cm² | 288 | 432 | 576 | 720 | 864 |
| 125 × 355 mm | 443 cm² | 319 | 479 | 639 | 799 | 958 | |
| Ø 250 mm | 125 × 400 mm | 500 cm² | 360 | 540 | 720 | 900 | 1080 |
| 200 × 315 mm | 630 cm² | 454 | 680 | 907 | 1134 | 1361 | |
| Ø 300 mm | 200 × 355 mm | 710 cm² | 511 | 767 | 1022 | 1278 | 1533 |
| 160 × 450 mm | 720 cm² | 518 | 778 | 1037 | 1296 | 1555 | |
| Ø 315 mm | 250 × 315 mm | 787 cm² | 567 | 850 | 1134 | 1417 | 1701 |
| 250 × 355 mm | 887 cm² | 639 | 958 | 1278 | 1597 | 1917 | |
| Ø 350 mm | 200 × 500 mm | 1000 cm² | 720 | 1080 | 1440 | 1800 | 2160 |
| 250 × 450 mm | 1125 cm² | 810 | 1215 | 1620 | 2025 | 2430 | |
| Ø 400 mm | 250 × 500 mm | 1250 cm² | 900 | 1350 | 1800 | 2250 | 2700 |
When equipping housing with forced ventilation and the use of special equipment, the power indicators of the equipment are added to the list of calculated indicators - power, speed and volume of forced (or discharged) air.
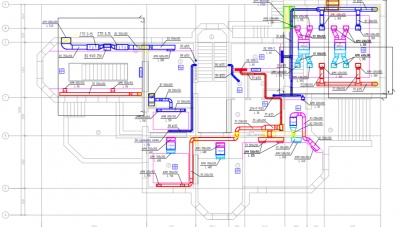
The design of the ventilation system is carried out on the basis of a floor plan, which displays all the routes and indicates the sizes and purpose of the functional elements
If ventilation planning is carried out at the design stage of the house, separate drawings are compiled with a calculation of all indicators and verification of their compliance with established standards. The project is certified by competent organizations and introduced with the general plan of measures for the construction of housing.
An approximate calculation of ventilation parameters can be carried out independently. To do this, you need to know the following:
- For every square meter of living space should be 3 m3 air for one hour.
- Each separate room (shared with the rest of the door) has its own specifics:
- a kitchen with a gas oven or water heater must be provided with a supply air of 70 m3/ h;
- kitchen with electric stove - 50 m3/ h;
- toilet “consumes” 30 m3 air per hour;
- bathroom - 50 m3/ h;
- entrance hall, wardrobe, pantry - 15 m each3 In one hour;
- living rooms - not less than 30 m3/ h
Sanitary standards provide for the calculation of the ventilation system taking into account the number of people who are constantly in the house. This small addition can significantly affect the overall picture of ventilation.
The calculation is carried out not only by the volume of air, but also by the number of people in the building
Based on these data, approximate duct parameters are calculated. It is taken into account that the average velocity of air outflow from the channel is 1.0–2.5 m / s. The diameter of the ventilation duct is selected taking into account the total air volume of the housing. As practice shows, for a one-story building with natural ventilation, an air pipe, depending on the volume of the internal space, should have the following dimensions:
- with a volume of 200 m3 - diameter of at least 18 cm;
- for a room of 400 m3 - 25 cm;
- if the interior of the house is 600 m3 and more - 32 cm.
These values can be used to calculate the air channel having a square or rectangular cross section, using the formula S = πR2where S is the cross-sectional area of the circle (expressed in m2), π is the number pi equal to 3.14, and R is the radius of the circle. Having found the value of the area of the circle, you can choose the size of the rectangular ventilation duct. At the same time, it must be increased by 20–25%, since the throughput of round pipes is always higher than that of rectangular pipes. The accepted ratio of the short side of the rectangle to the long 1: 3.

If rectangular ducts are used instead of round ducts, their cross-section must be increased by 20–25%
The use of forced ventilation - the installation of a discharge fan - reduces the required pipe sizes. This is due to an increase in the air velocity in the channel. So, for rooms with a volume of 200, 400 and 600 m3 canals with diameters of 11, 18 and 23 cm can be used, respectively.
Video: do-it-yourself ventilation in the basement
Pros and Cons of Natural Ventilation
The main advantage of natural ventilation is that its installation does not require large financial costs.
Once installed, the vent system does not require frequent maintenance.
She works as much as the house costs. The design of this type of ventilation is simple and rarely leads to any complications or accidents. There are no electrical devices inside the system that increase background noise. The movement of air occurs naturally, without mechanical pressure. The pluses include good compatibility of natural ventilation with other ventilation methods. Most often, it is a combination of natural and forced ventilation systems that gives optimal results.
Cons of the natural ventilation system:
- There is no way to adjust the rate of air flow. This can cause moisture and moisture to stagnate inside, leading to mold and mildew.
- Through inflow channels, dust and insects freely penetrate inside. This reduces comfort and leads to more frequent cleaning indoors. In part, this can be compensated by installing mosquito nets, but it should be borne in mind that this also reduces the permeability of clean air.
- Heat losses are high in the cold season.Some experts claim that the figure can reach up to 40%.
- Weather dependent. The higher the air temperature outside the house, the less efficient the ventilation.
Interestingly, in hot Mediterranean countries, such as Spain, Italy or Portugal, ventilation in residential buildings is arranged by the so-called patios - patios in the form of a vertical well. The sun practically does not penetrate the patio, and all windows and balconies face this direction.
Video: Natural ventilation at home
Improving natural ventilation
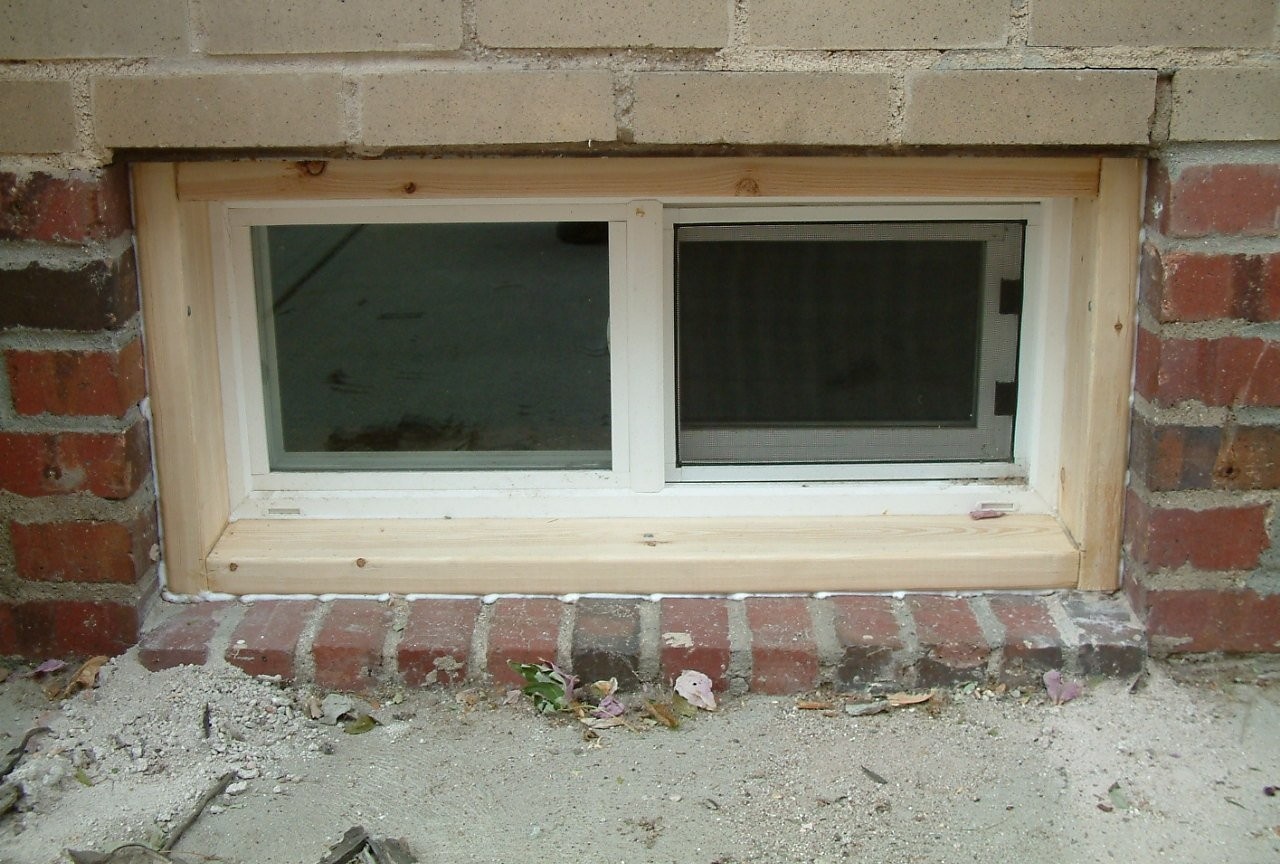
It is possible to significantly increase the efficiency of natural ventilation by installing supply air valves on the windows. Their cost is low, and installation is simple and affordable for self-fulfillment. Most often, such devices are used for plastic windows. The fact is that the double-glazed window connects to the frame quite tightly, and this sometimes turns into the negative side - moisture accumulates in the room, mold may appear. To compensate for this phenomenon, inlet valves were developed, with the help of which it became possible to regulate the degree of ventilation through the window. The device is installed in the upper part of the frame. Due to its small size, the installation of the valve does not affect the reduction of the light flux through the window.
A supply valve is part of the natural ventilation that supplies fresh air into the room. The principle of operation of the device is based on the hygroscopic properties of some materials (special nylon tapes), which under the influence of moisture change their linear dimensions. The valve automatically changes the air supply (but some models also have manual control). This happens due to the narrowing or expansion of the airway leaf.
Types of Supply Valves
There are metal and plastic devices. Metal valves are reliable in operation, but at the same time they are more expensive and have a large mass.
These devices are usually divided into two categories:
- mechanical. The operating mode of the mechanical integrated valve is set manually. The optimal valve position in each specific situation is found by the selection method. As temperature and atmospheric pressure change, an adjustment is made to achieve an acceptable result. The mechanical valve kit includes a sturdy cord that attaches to the control lever. Due to this, the device can be manipulated from its normal position, standing on the floor;
- automatic. These devices are factory calibrated. The initial parameters are set so that the hygroscopic sensor regulates the degree of narrowing of the valve as necessary, without human intervention. Changes in temperature, humidity, wind force in the environment are detected by a sensitive sensor, which brings the level of natural ventilation to the desired state. In order to prevent condensation from forming inside the slit valve, the design is designed so that air does not meet outside with internal flows.
When using mechanical devices in the winter, it should be remembered that the valve cannot be completely closed - it can freeze. And when you try to open it with physical effort - to break.
Supply valve installation
As noted above, the installation of the device does not require special skills or tools. Each product is accompanied by detailed instructions, following which you can install the device yourself.
For this we need:
- construction knife;
- screwdriver;
- roulette.
The kit for installation includes:
- supply valve;
- fixture;
- sealant.
Installation on the window is carried out in several stages:
- The frame is marked under the valve mount. The device is usually located in the middle.
- The marked window seal is cut off.
- Dimensions from the frame are transferred to the surface of the sash. The seal is also cut off and removed.
- In the formed groove of the sash of the window, 3 small segments of the seal are inserted. They are placed in places intended for fixing the valve with screws.
- The supply valve body is freed from the protective film, a double-sided tape is prepared to fix the device to the frame.
- The ventilation device is first fixed to the tape, and then - with self-tapping screws through the prepared holes.
- In the intervals of the fortified sections, a seal is laid.
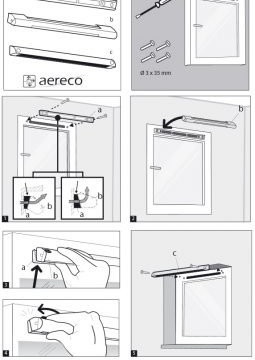
The supply valve is usually installed in the upper part of the window frame and is attached to the plastic profile using self-tapping screws
Video: why breathing is hard in the house
How to make ventilation yourself
Each house is a separate story with its own characteristics and architectural nuances. If the house has already been built, then there will be such ventilation in it that will arise naturally. Correcting the situation is possible only with the help of coercive measures - mechanical or combined. Let's pay attention to the main requirements that a ventilation system must meet:
- Properly functioning ventilation should not lower the room temperature in the cold season.
- Sustainable drafts should not occur in the house.
- “Exhausted” air from kitchens, bathtubs and toilets must be quickly removed from the premises and replaced with fresh.
- The circulation should capture all rooms without exception - pantries, basements, corridors, etc.
- The system should provide a constant flow of fresh and stale air.
The surest solution to all issues related to ventilation is to set up a circulation system at the planning and construction stage of a house. One or two channels of natural ventilation are designed depending on the size of the living space, the location of the office space and the number of people living in the house. They are vertical shafts that rest on the foundation of the house and are displayed above the roof. It is realized with the help of various construction technologies.

The dimensions of the ventilation riser in apartment buildings are calculated according to the standard method
One of these solutions can be laying ready-made ventilation units in a load-bearing wall. Another option is an independent ventilation duct made of brick. Indoors, large-diameter metal pipes are used to create air mass flows. For aesthetic reasons, they are hidden under suspended ceilings or inside walls. Decorative plastic grids are installed at the ends.
The same grilles are mounted in the lower part of the door leaf, if the room is dull, has no windows and is not accessible for ventilation. In homes that are heated by stoves, a chimney can play the role of a ventilation shaft.
Tips from experienced craftsmen on organizing ventilation in the house
Here are some recommendations that summarize the experience of installing systems of various configurations on a variety of objects.
Designing a ventilation device before starting construction
These tips will help those who plan to install ventilation from scratch.
- The optimal location of the ventilation shaft is the central part of the structure. In the cold season, the temperature difference inside the room will always be higher, which will lead to increased air draft.
- The installation of a ventilation riser is best tied to a load-bearing wall - it will always be warmer in it than in other places, which will create additional conditions for the movement of air masses.
- When choosing ducts, you need to take into account the specific situation. If there is enough space, you can install round ducts. They work great, creating intense traction. If installation occurs in cramped conditions, rectangular channels are better suited - they take up less space and are more compact in installation.
- When choosing round channels, you should know that rigid pipes work more efficiently - air moves through them without encountering resistance. Corrugated pipes can make noise, but they are much easier to install. Experts advise using hard pipes whenever possible, resorting to corrugated pipes only in case of emergency.
- It is necessary to use exhaust air ducts of the same diameter. Constrictions and extensions adversely affect the speed of air movement. If deviations are inevitable, they should be made with smooth bends of the pipe.
- The wider and higher the riser of the main shaft, the better the ventilation will work.
- All pipe connections in the system must be made even and smooth. Roughnesses and roughness inside the pipe create a noticeable resistance to the passage of air.
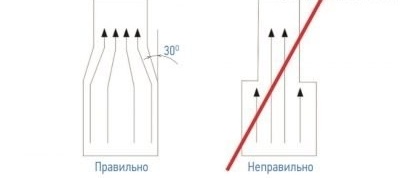
- The system should have as few turns as possible in the horizontal and vertical plane. Any rotation reduces the air speed by 10-12%.
Tips for upgrading existing ventilation
If the house was built a long time ago, but ventilation for some reason has ceased to satisfy the needs of residents, use the little tricks that improve the system.
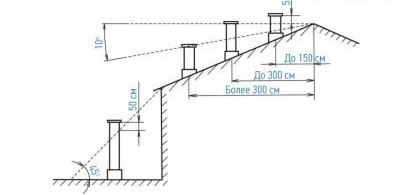
- Installation of a deflector on the top of the ventilation shaft enhances draft by 15–25%. In addition, the canal is reliably protected from debris, insects and rain with snow.
- Sealed windows made of plastic and double-glazed windows interfere with ventilation in a natural way. The use of supply valves with humidity sensors will solve this problem. They do not have to be installed on all windows - just one for a separate room.
- In a house with stove heating, chimney pipe provides natural ventilation. At a time when the furnace is not heated (for example, at night), you can leave the blower and chimney valve open - air convection will occur through them.
- Additional devices that increase the efficiency of the existing natural ventilation system can be small air intake devices with built-in fans. These are breathers and ventilators. They can be applied locally.
In wooden houses, it is very important to ventilate the underground space, which is in direct contact with the ground.
To do this, vents are arranged along the entire perimeter of the outer walls. But another good solution is to bring the air intake to the underfloor from the ash pan of the furnace. In this case, during combustion of the furnace, air will be taken from the underground space.This achieves the solution of two important problems at once - ventilation of the underfloor and heat preservation in residential premises (in normal furnace mode, combustion air comes from the living area).
Without food, a person will survive a month and a half. Without water - a week. Without air, only trained yogis can live more than 15 minutes. Caring for clean air is a key condition for a healthy and fulfilling human life.