Kuznetsov's furnace: step by step instructions for manufacturing

Ideas for the creation of ultra-efficient furnaces by I.V. Kuznetsov are borrowed all over the world, including the USA and Europe. To make one of the furnaces according to the Kuznetsov model with a responsible approach, you can do it yourself.
Content
Kuznetsov furnace application
For many years of inventive activity, I.V. Kuznetsov has developed about 150 models of furnaces designed for use in all areas of human life without exception, where heat generation is required. By type of specialization, "blacksmiths" are:
- heating;
- cooking;
- heating and cooking;
- bath
- outdoor, intended for smoking products, barbecue and cooking on the grill;
- fireplaces with an open firebox, allowing to admire the flame.
Advantages and disadvantages
The wide popularity of Kuznetsov furnaces and the deep respect that people who know about the furnace business have for them are due to several advantages:
- The efficiency of the “blacksmiths” exceeds 80%, and in some models it can reach 95%.
- The furnaces operate in high temperature mode, but at the same time dispense with materials and technologies available only in the factory.
- The high temperature mode allows you to heat the furnace even with the most waste and low-quality fuel.
- Again, due to the high combustion temperature, the fuel is oxidized in almost full volume, therefore, soot is formed in minimal quantities. The oven may not require cleaning for several years.
- The design of the furnace provides a very uniform heat transfer between the furnaces, while it takes less material than during construction using traditional technology.
- In furnaces equipped with a heat exchanger, heat for heating water is taken from the flue gases, and not from the furnace, so that the blacksmith can easily perform the function of a boiler without compromising performance.
- The principle of operation of the furnace provides good traction, so there is no need to build a high chimney.
- “Kuznetsovka” is very plastic both in terms of design and in terms of design. That is, it can easily be adapted to any room without sacrificing performance and efficiency.
- The furnace is designed in such a way that after the furnace its chimney does not need to be covered with a view. Carbon monoxide poisoning is completely eliminated.
- The design assumes an even distribution of heat in the furnace body, therefore, cracks from local deformations do not develop in the masonry.
What about the flaws? Technically, they are not, but something needs to be taken into account.Kuznetsov's furnace cannot have massive walls - this would negate many of its advantages. But at the same time, it is subjected to rather high thermal loads. Therefore, this unit must be carefully calculated and verified at the development stage and built with the same meticulous observance of all the requirements of the technology. At the slightest deviation from the technical regulations, the Kuznetsovka will turn out to be very short-lived.
You can also add a Russian stove yourself if you follow the detailed instructions. You will find them in our next article:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/otoplenie/russkaya-pech-volshebstvo-sozdannoe-svoimi-rukami.html.
Design and principle of operation
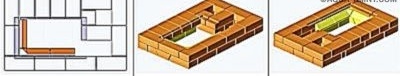
The inventor I.V. Kuznetsov took as a basis a bell-type furnace, known for its cost-effectiveness.
The high efficiency of such furnaces is due to the nature of the movement of flue gases. If in ducted furnaces they are pulled into the chimney, often not having time to give heat to the brick mass, then in bell-shaped stoves they swirl for a long time under the hood's arch until they cool down. Only then do they go down to the outlet, from where they then enter the chimney. A cap filled with gases plays the role of a view along the way: cold air from a chimney cannot penetrate into it, just as water cannot fill an inverted diving bell. This effect is called the gas view.
The inventor worked with a sophisticated version of such a furnace having two caps.
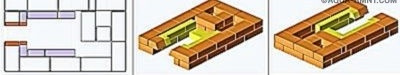
Diagram of a two-bell model
As you can see, the caps are connected in a sequential manner, that is, the selection of heat of the flue gases occurs in a two-stage scheme. Previously, the construction of furnaces with such a design was not very readily taken - not only because of the complexity, but also some undesirable features. So, for example, the thrust in the second cap can easily break the gas plug in the first, negating the effect of the "gas view".
The master dealt with this drawback as follows. The furnace was equipped with so-called bottom channels, laid bypassing the heat-accumulating parts of the array. While the flame burns in the furnace, the convective flow formed by it ensures the operation of the traction in the normal mode. When the fuel is consumed and convection stops, the draft itself will be redistributed in such a way that the cold air stream will follow through the lower channels, and not through the heated body of the furnace.
This solution not only compensated for the instability of the gas view, but also turned out to be more reliable: the cork formed by gases can be pulled out by a strong gust of wind, while in Kuznetsov’s furnace the draft is redirected away from the hot massif under any conditions. In addition, due to the presence of grassroots channels, there is no need to arrange ventilation of the room.
Read also our article on the construction of a Dutch brick oven:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/otoplenie/pech-gollandka-rukovodstvo-po-izgotovleniyu-dlya-domashnego-mastera.html.
How does it work
Here is the sequence of processes in the Kuznetsov furnace:
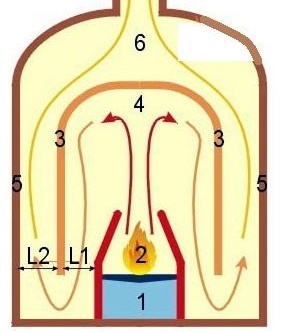
- Due to the air entering through the blower (pos. 1) in the furnace (pos. 2), fuel is burned, the resulting mixture of flue and pyrolysis gases rises into the lower hood (pos. 3). Under its vault (item 4), the pyrolysis gas finally decomposes into combustible components, which burn here. This design provides the effect of self-regulation: with strong burning of the flame, the gas plug increases and blocks traction; due to the weakening of the draft, the combustion in the furnace also weakens, the gas plug cooling down decreases and the draft resumes.
- Conditionally cold gases from the lower hood enter the upper one (item 5). If the furnace is round (this is an ideal form for a two-bell scheme), then the body plays the role of the upper bell. In its upper part (pos. 6), the oxidation of carbon monoxide and nitric oxide occurs, so that it enters the chimney (pos.7) the exhaust mainly consists of carbon dioxide and water vapor. The gases entering the second hood are no longer super-hot - temperatures from 200 to 400 degrees - and chemically aggressive, so you can install a water heat exchanger from ordinary structural steel. The selection of heat for water does not change the operation mode of the furnace, since the high-temperature part - the firebox + lower hood - is insulated with a brick wall.
Due to the high combustion temperature, the chamotte firebox in Kuznetsov's furnaces should be made isolated from the main massif or, as they say, floating. None of its elements should be embedded in ceramic masonry, otherwise the latter, even if there are expansion joints during the furnace, will break - the difference in the coefficients of thermal expansion of these materials will affect.
The firebox should be surrounded by a so-called dry joint. This is a seam between fireclay and ceramic bricks, which instead of clay mortar is filled with a gasket made of asbestos or basalt cardboard.
An annular gap (L1) is arranged between the furnace and the lower hood and another (L2) - between the hoods. If the width of L2 is made larger than that of L1, the gas view will be more stable.
Calculation of the Kuznetsov furnace
Kuznetsovka is a very complex heating device and attempts to calculate it and design it yourself will not lead to anything good. You just need to choose from all the available options the most suitable for yourself - the author does not make secrets from his achievements. If the characteristics of the model you like do not indicate the heat transfer capacity, it can be calculated approximately: a furnace that is heated twice a day, each sq. m of its surface gives off about 500 watts of heat.
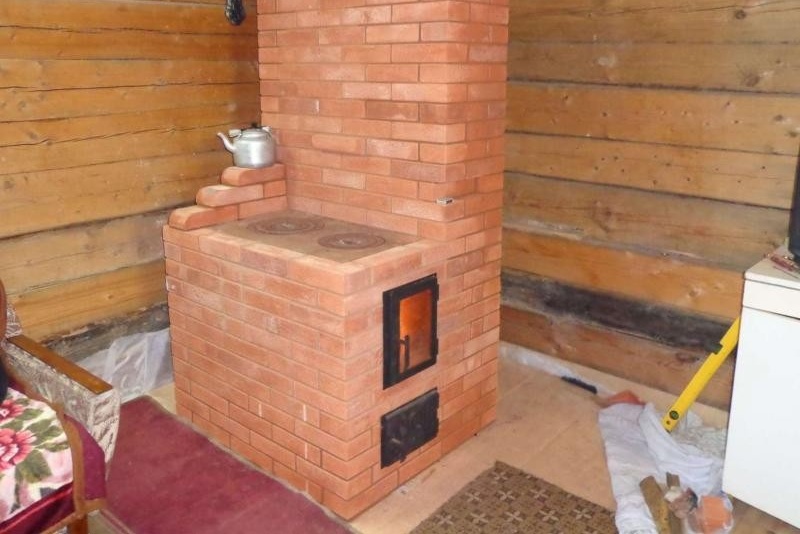
The OVIK-9 furnace, the manufacturing procedure of which we will consider, with dimensions of 1015x630x2100 mm, has a heat transfer capacity of 3.6 kW.
Preparatory work
First of all, you need to choose a place for the construction of the furnace. It is easiest to do this before the house is built - then both the stove and the building are designed together so that three or at least two rooms are heated. With a ready-made house, the situation is more complicated. In this case, they try to build the furnace into the interior partition, since introducing it into the load-bearing wall requires complex calculations and dangerous labor-intensive work (part of the wall will have to be dismantled, keeping the load from overlapping by a system of jumpers and columns).
You can, of course, limit yourself to a simple wall-mounted variant of location, but then only one room will be heated.
A reinforced concrete foundation needs to be built at the selected location. Its dimensions must exceed the dimensions of the furnace by at least 100 mm on each side. The combination of the foundation of the furnace with the foundation of the building is not allowed - both structures give different draft and one of the bases will pull the other along with it, causing it to skew.
The depth of the foundation depends on the bearing capacity of the soil, the depth of its freezing, the method of operation of the building (periodically / constantly). Typically, in buildings with year-round living of people located on stable soil, the foundation is buried by 400-600 mm. At the bottom of the excavation, crushed stone should be poured as a strengthening layer, and a sand cushion over it.
Then they do everything according to traditional technology - install the formwork, fix the reinforcement cage and fill it with concrete. It is only necessary to proceed to the construction of the kiln after the concrete has fully matured and it has set sufficient strength - this usually takes about a month.
Before laying the 1st row on top of the foundation, you need to lay a waterproofing of two layers of roofing felt or roofing. The contours of the future furnace are applied with chalk on it - it will be easier to navigate this way.
Materials and Tools
For work you will need:
- trowel;
- level;
- mallet and other construction tools.
To divide the bricks, you need a pickaxe and a grinder with a diamond wheel.
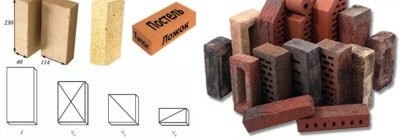
The furnace will be built of two types of bricks: a regular ceramic full body with a brand of M150 (250x120x65 mm) and fireclay grade SHB-8 (250x123x65 mm) or Sh-5 (230x114x40 mm). The firebox walls will be laid out with fireclay bricks.
When purchasing fireclay bricks, you should be very careful. Unscrupulous sellers can give him an acid-resistant brick, which is similar in appearance but does not withstand high temperatures. So it will not be superfluous to ask for a certificate.
It is often recommended to choose fireclay bricks by color - the darker the better. But such a rule is not always valid. If clay used in different deposits was used, then the characteristics of light brick may well be higher than that of dark brick. It is more correct to evaluate the quality of fireclay bricks according to the following criteria:
- the structure should be homogeneous and fine-grained - without pores and inclusions visible to the naked eye;
- when tapping with a metal object (light hammer or wrench), the brick should make a clear jerky and loud sound;
- when falling, it should break into large pieces (low-quality crumbles into small fragments up to sand).
For a structure with dimensions of 1015x630x2100 mm, 430 ceramic bricks (excluding the chimney) and 22 chamotte will be needed.
How to prepare a solution
The solution is clay. Clay and sand used for its preparation should not have organic impurities, which can lead to cracking of joints. In clay, the presence of these impurities can be recognized by a clearly audible smell (it can even be pleasant) - normally the clay smells almost nonexistent.
Sand should be used either mountain or made by grinding brick fight - in these varieties the content of organic impurities is minimal, or they are completely absent. Brick sand is usually cheaper than mountain sand, but not inferior in quality. Just pay attention to the following circumstance: for a mortar of ceramic masonry, sand from ceramic brick is needed, and for chamotte, respectively, from chamotte.
Pay attention to the grade of clay. The solution for chamotte masonry should be prepared on the basis of white kaolin or chamotte marl. For clay masonry, any clay with refractory properties is suitable, for example, gray or blue Cambrian, gray kaolin.
Clay of the same grade, but from different deposits, can vary greatly in viscosity, fat content and adhesive properties. Therefore, the recipe for the solution, namely the optimal ratio of sand and clay in it, should be selected empirically. In the case of brick sand, this is done as follows:
- A portion of clay weighing 1 kg should be poured to the top with water and left for a day.
- After this, the deoxidized clay is kneaded with the addition of water until it becomes like plasticine or thick dough and stops sticking to your hands.
Then the clay is divided into 5 equal portions, in each of which a certain amount of sand is added:
- in the first - 10% of the clay volume;
- in the 2nd - 25%;
- in the 3rd - 50%;
- in the 4th - 75%;
- in the 5th - 100%.
Each portion must be thoroughly mixed until smooth and dried for 4 hours. Remember to mark how much sand is contained.
After this, each portion of the solution by rolling out needs to be shaped into a cylinder 30 cm long and 1–1.5 cm in diameter. All of them are wrapped around a round blank about 5 cm in diameter. Now the test samples must be dried for two weeks at room temperature and without drafts .
After this, it remains to evaluate each of the options:
- If there are no cracks on the cylinder at all, or if they are in the form of a very fine mesh, such a solution can be used for any part of the furnace.
- If the depth of the cracks reaches 1–2 mm, the solution can withstand temperatures up to 300 degrees. Such a mixture can be used for laying a country fireplace or barbecue.
- In the presence of deep cracks or tears, the solution is deemed unsuitable for use - the proportion of sand present in it is excessive.
Typically, about 0.2 cubic meters is spent on laying 500 bricks. m mixture of clay and sand.
Note! If you do not mind the additional costs, you can purchase a ready-made mixture for preparing a stove solution in a specialized store.
Having thus determined the optimal combination of clay and sand, they begin to prepare the solution:
- the necessary amount of clay (about 40 kg per 100 bricks) is again soaked for a day, kneaded until the test is consistent, but after that it is still rubbed through a sieve with a 3x3 mm cell;
- then, according to a formulation selected experimentally, sand is added;
- gradually adding water, the solution is stirred to a creamy state;
- evaluate how the solution wets the trowel, and if necessary, adjust its composition by adding a small amount of clay or sand.
What else is needed
- A furnace door, for example, of the DT-3 brand, with an opening size of 250x210 mm.
- An under-door, for example, of the KDP brand, with an opening of 250x140 mm
- Grate with a size of 250x252 mm.
- Cooktop made of cast iron on two burners, size - 586x336 mm.
- Doors measuring 510x340 mm in an amount of 2 pcs. - for the cooking chamber.
- Gate valves with a bore 130 × 130 mm in the amount of 2 pcs. - for a cooking chamber and for switching between summer and winter operating modes.
- Gate valve with a clearance of 250x130 mm - for the chimney.
- Sections of an equal-shelf angle 36x4 with a length of 600 mm (4 pcs.).
- A piece of steel strip 40x4 mm, length 600 mm.
- Steel sheet 3 mm thick, size 600x550 mm.
- Steel sheet with a thickness of 3 mm in size 500x700 mm to protect the floor in front of the furnace.
Steel should be replaced with any other fireproof flooring, for example, ceramic tiles.
Ever dreamed of having a magical fireplace in your home? You can fold it yourself. And the following guide will help with this:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/otoplenie/uglovoj-kamin-svoimi-rukami-poshagovaya-instrukciya.html.
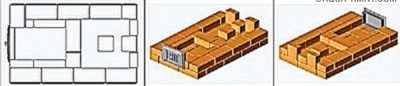
Masonry: ordering and step-by-step instructions
The sequence of work looks like this:
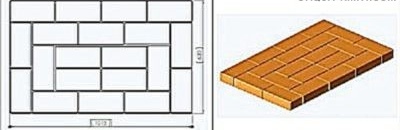
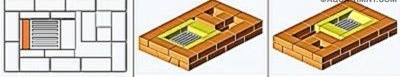
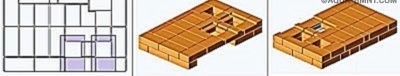
Spread the first row of 20 bricks, which should be a perfect rectangle with a strictly horizontal surface.
“Rectangle” is checked by measuring the diagonals - they must be equal. In the absence of experience, the series must first be laid out without a solution, and only then, when everything is adjusted and checked, apply the solution. The thickness of the seams should be 5 mm.
Tip. To make the stove look more attractive, install rounded bricks in the corners. They do not have to be cut yourself - such blocks are sold ready-made.
In the 2nd row, the first (lower) hood and the blower chamber originate. Two halves of the brick are laid without mortar and slightly pushed out. When the masonry is completed, these bricks will need to be removed, which will make it possible to clean the base of the hood of spray mortar and brick fragments. After cleaning, the halves are finally placed on the solution.
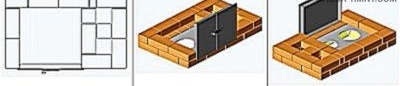
When the 2nd row is laid out (14 bricks are required), a blower door is installed on it, supporting it with several bricks. The door frame must be wrapped with an asbestos cord, which will simultaneously act as a sealant and a temperature joint. It is fixed in the masonry by means of a wire, which is laid in the seams.
It is recommended to use wire for reinforcing the walls of the furnace, laying it in the seams of every second row.
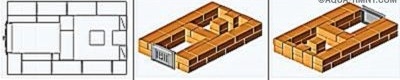
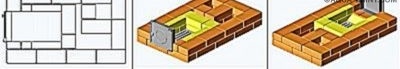
Having laid out the 3rd row according to the scheme (the bricks included in its composition should tightly fix the blower door), proceed to laying the 4th. Here, in addition to ceramic bricks, fireclay is used - we begin to lay out the side and back walls of the furnace.
The basement door is blocked by hewn ceramic bricks looking outward and chamotte chamois looking inward. They must be separated by a thermal gap of 5 mm.You can arrange it in the following way: between the bricks, a laying of packing corrugated cardboard is laid - it just has the desired thickness; upon kindling, the cardboard will burn out and the gap will form by itself. Temperature gaps must be provided everywhere where fireclay bricks are adjacent to ceramic.
In row No. 5, the fireclay bricks that form the side walls of the furnace are slightly shifted so that the bricks of the 4th row below them form a shelf with a width of 10-15 mm for the grate. The bricks should be moved apart so that between them and the grate there remains a gap of 5 mm, necessary for the free expansion of the heated metal.
The brick forming the front wall should be trimmed at random.
In the same row, the formation of a vertical channel connecting both caps begins.
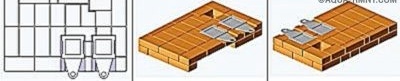
When the row is laid out, you should install the grate on its place, filling the gap between it and the bricks with sand.
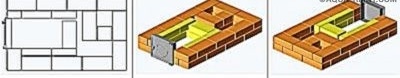
In parallel with laying the 6th row, you need to install and fix the furnace door. Direct contact of its frame with a brick is not allowed - it is necessary to lay asbestos cord as a gasket. From below, the door frame can be fixed with wire, but a more reliable element is required from above - the wire will quickly burn out. Instead, a steel strip is used.
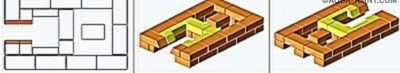
When laying row number 7 on the side of the brick forming the back wall of the furnace, a gap of 20–30 mm wide is left. This is the beginning of a dry seam.
After laying out number 8 according to the scheme, they begin laying the 9th row. At this stage, a channel is formed connecting the firebox with the lower hood. Lilac color indicates bricks in the side walls of the furnace, the upper edges of which should be 10 mm below the plane of the row. It will be necessary to lay an asbestos strip 10 mm thick on the left wall so that it is flush with the row plane.
Pay attention to how the furnace door is closed: the bricks are cut at random so that the “lock” masonry is obtained.
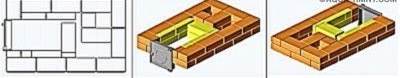
Laying out the 10th row, it should be remembered that on the asbestos lining (it covers the fireclay bricks in the furnace wall), ceramic bricks must be laid without mortar.
In the ceramic bricks surrounding the firebox, it is necessary to cut out under the hob. Its dimensions should be such that around the slab there remains a temperature gap of 5 mm, that is, the bricks will need to be cut by about 10 mm. And in the contact zone of the hob with fireclay bricks, it is necessary to leave a gap of 10 mm. Such bricks, trimmed at random, are located in front and on the right (marked in orange).
If the slab is equipped with stiffening ribs from below, for them it is necessary to additionally cut out grooves in the brick so that the slab is supported on the brick along the entire edge. Install it immediately after laying the row - on an asbestos cord soaked in clay solution. The gaps between the slab and the bricks are filled with sand.
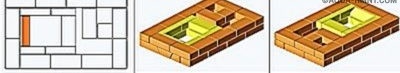
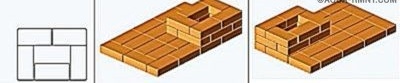
Near No. 11, the walls of the cooking chamber begin. A door for it is also installed here, the frame of which must be wrapped with an asbestos cord. To fix, you can again use the wire.
Rows 12, 13 and 14 do not need comments - just lay out according order.
After laying the bricks of the 15th row, the cooking chamber is blocked by a steel sheet 3 mm thick and 600x550 mm in size with a cutout for the exhaust duct. The top of the sheet is hardened with 4 pieces of corner and a steel strip. Steel flooring eliminates the ingestion of various small debris that could be poured into it from masonry.
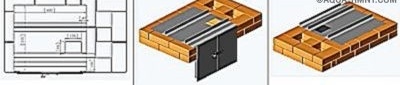
In the bricks of the 16th row, framing the exhaust and front vertical channels, cuts are made for the valves, taking into account the 5-mm temperature gap.
When the row is laid out, the valves are installed in place.
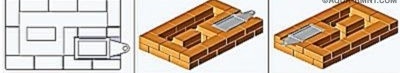
After the 17th row, the formation of the upper cap begins (18th row). Here, it is also necessary to leave slightly extended halves without a solution, removing which, it will be possible to clean the base of the hood from the mortar and various debris that fell during masonry. After cleaning, the extracted bricks are coated with a solution and finally installed in their place.
Rows from the 19th to the 27th are laid out according to the order.
In the 28th row, the main chimney gate is installed. Under it, in bricks, cuts should be made 10 mm deep (marked in lilac) and of such a width that a temperature gap of 5 mm remains around the valve body.
The valve must be installed immediately after laying the row, and it fits on the solution.
In series No. 29 and 30, the furnace is closed, and next to No. 31, a pipe with a flue channel into the brick (270x140 mm) begins.
The finished oven must be thoroughly dried. To do this, it is maintained for some time with fully open doors and latches. Things will go faster if you hang a light bulb with a power of 200-400 watts in the furnace. It will provide not only heat, but also a steady convective flow, which will remove all moisture in a short time.
The first furnace should be produced with a small portion of fuel - the fire must first harden the walls of the furnace.
Do not tackle the furnish of the furnace before it has fully completed the first season - the decorative coating may be damaged during shrinkage processes.
Operation in various modes
In summer mode, Kuznetsov’s stove turns from a heating and cooking stove into a cooking stove. To do this, it is enough to open a special valve (it is called the summer valve), after which the flue gases will enter the chimney directly, bypassing the caps. Accordingly, only the hob will be heated.
The temperature inside the cooking chamber can be controlled by a valve installed on the exhaust duct extending from it. By closing the gate valve and the chamber door, it can easily be turned into an oven. For ease of use, the shelves for the baking sheet can be fixed in the walls.
If you need to quickly warm up the room or dry out, the door of the cooking chamber is opened. At the same time, the temperature on the burners remains high enough for cooking.
Video: DIY do-it-yourself stove construction - part 1
Video: Part 2
Kuznetsov's furnace has the highest technical characteristics, but at the same time it is quite accessible for the master in the novice class. But experienced stove-makers should be careful - they often overestimate their knowledge and do something in their own way, neglecting the recommendations of the inventor. Such deviations are not allowed - as was said, the Kuznetsov furnace is calculated with high accuracy and should be built just as accurately. Follow the instructions in the article and you will be protected from errors.