How to make fresh air ventilation in a private house with your own hands: the principle of work, design and installation

Ventilation and heating are the systems responsible for creating a comfortable microclimate inside the living room. But about ventilation, property owners often remember in extreme cases. Usually this happens when it becomes difficult to be in a living room, health and sleep worsen. Then people turn to specialists who, at the first inspection of the structure, indicate poor air exchange.
Content
What is ventilation in a private house for?
The process of indoor air exchange is closely related to the life of people. Ventilation provides the sanitary and hygienic conditions necessary to maintain a person in good shape, preserve his health and well-being. It also performs the following functions:
- removes accumulated volumes of carbon dioxide and fills the room with oxygen;
- maintains clean air, reducing the level of particles hazardous to human health;
- removes unpleasant odors from the room - physiological secretions of the body, perfumes, the smell of cosmetics and household chemicals;
- normalizes the general level of humidity in the room.
Constant high humidity is the main cause of the formation of mold and fungi that are dangerous to human health, and also reduces the service life of electrical appliances, worsens the appearance of finishing materials and furniture.
The list of problems from the lack of ventilation or its incorrect operation can be continued, but the above is enough to understand the importance of this system. Its type and installation methods are thought out at the design stage of a residential building. If for some reason a private house or cottage is not equipped with a ventilation system, we recommend that you begin to equip it as soon as possible.
Special requirements are imposed on ventilation systems installed in houses where gas boilers are provided. You can learn more about this in our article:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/ventilyaciya/ventkanal-dlya-gazovogo-kotla-v-chastnom-dome.html.
Types of ventilation systems
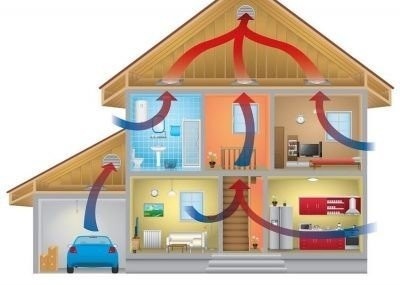
In a private house, the following types of systems are used (a set of ducts and equipment for cleaning, heating, cooling, transporting, supplying and replacing air):
- Natural - air exchange is achieved by the pressure difference inside and outside the building. It does not require large expenditures for the purchase of equipment and maintenance, since electricity is not needed for work. Its effectiveness directly depends on the temperature and purity of the air outside the house, the speed of the air flow and their direction. This is its main drawback, since the air is supplied in such a condition and at such a temperature as it was outside the house.
- Forced - air exchange occurs due to the pressure difference created by special equipment. Various devices are used for work: fans, air heater, noise absorber, filters, electric motor and others. This allows you to treat the air to the desired condition and supply it to the room in the volume that is required for normal human life. The disadvantage of a mechanical system is its high cost and maintenance costs.
For the arrangement of a private house, it is recommended to use mechanical (forced) ventilation, even despite the general costs of its operation. It can be combined with natural, which will only increase efficiency.
The rooms in the apartment also need good ventilation, especially when it comes to the bathroom. In such rooms a venal channel is provided where a special fan can be installed. You will find material with step-by-step installation instructions here:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/ventilyaciya/ustanovka-ventilyatora-dlya-vytyazhki-v-vannoj-komnate-svoimi-rukami.html.
Varieties of forced ventilation systems
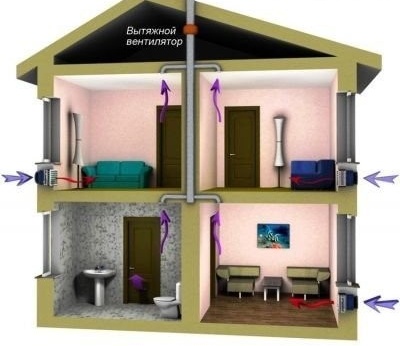
According to the method of air exchange, forced ventilation is divided into two types:
- Local (a set of ducts providing an influx of fresh air to a specific place). The delivery of clean and the removal of polluted air occurs only in the room where the canal is led out.
- General exchange (allows you to create the same conditions in all rooms of a residential building due to the system of combined air ducts connected to each of the rooms).
By appointment, it is classified into the following varieties:
- supply - is used to supply a volume of air that can be heated or cooled to a certain temperature;
- exhaust - used to remove contaminated air, combustion products, steam;
- supply and exhaust - provides simultaneous supply of fresh and removal of exhaust air.
For the arrangement of a private house, it is recommended to use forced ventilation. The system provides the most efficient ventilation, taking into account the temperature and air parameters in the room.
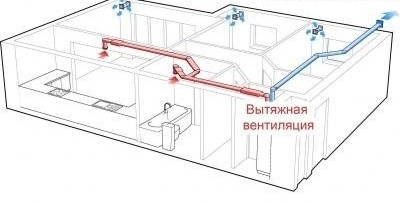
Supply and exhaust ventilation in the apartment provides a simultaneous supply of fresh and exhaust air
Design and device of forced ventilation
According to the method of the device, the supply system can be:
- duct (air is delivered to the room through pipes and metal ducts);
- channel-free (compact equipment in the form of a valve that is mounted in a hole in the wall).
Typesetting and one-piece systems
The channel supply ventilation includes typesetting constructions (consists of separate equipment that is mounted along the channel path) and monoblock (parts are placed in a closed case, protected by noise insulation material) type.
A type-setting installation is usually mounted under a suspended ceiling, in the attic or in a special space reserved for laying communications. It allows air purification in rooms of any type and size. The only drawback is the complexity of its device and the large dimensions. The supply ventilation of the type-setting consists of the following elements:
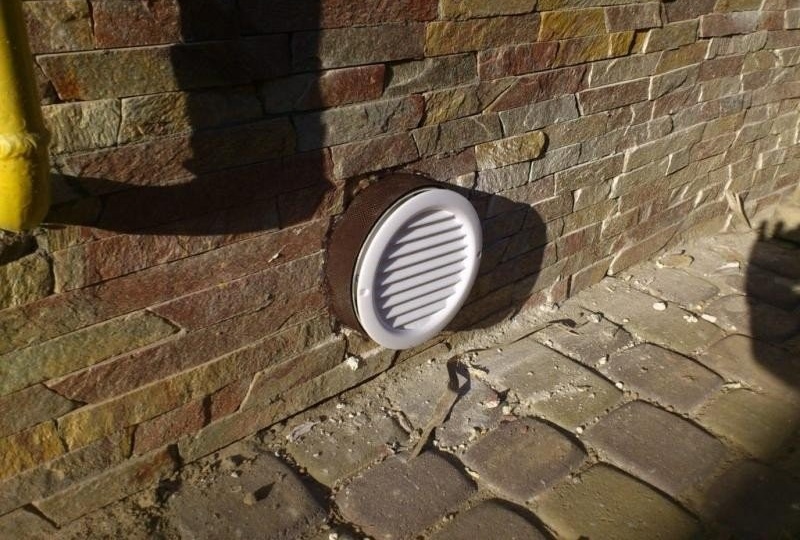
- Air grill. It is mounted on the outside of the building, it is necessary to take in fresh air and protect the channel from large debris.
- Air valve - a device that controls the amount of intake air. Prevents the entry of cold air when the heating equipment is turned off. According to the method of operation, the valves are divided into mechanical (spring) and automatic with an electric actuator (more efficient and reliable, since they are guaranteed to block the air supply after turning off the air heater).
- The filter protects equipment and ventilated rooms from particles of small debris, dust, bird and animal fluff. According to the degree of purification, they are divided into coarse filters (retains particles larger than 10 microns), fine (up to 1 microns) and especially fine (up to 0.1 microns) filters.
- Air heater - electric or water heater. It is mounted in the ventilation duct and serves to heat cold air to the desired temperature. The electric type is used in systems of small power, and the water type is used in the ventilation of a country house, office or other premises of a large area.
About the choice of heaters for the supply ventilation system, read in our article:https://aquatech.tomathouse.com/en/otoplenie/kalorifer-vodyanoy-dlya-pritochnoy-ventilyatsii.html.
- The evaporator is used to cool the supply air. Commonly used in a combined system. By the type of coolant, freon and water systems are distinguished.
- The fan is the main element of the system, providing an even supply of fresh air in the required volume. It is selected taking into account the norms of air exchange, system power and pressure.
- A silencer prevents the propagation of noise through the ventilation duct from the operation of the fan and other equipment.
- Duct - an element of the air duct network (channel) used for transporting air. It is selected taking into account the cross-sectional area, shape and stiffness of the element.
- Switchgears are used to manually adjust the volume of air flow. They are mounted at the outlet of the duct from the side of the room and are a grille or diffuser.
- Automation system - a ventilation system control device. It consists of a regulator behind the fan speed, a temperature control unit, a thermostat, a hydrostat, etc.
The monoblock installation produces less noise, which makes it possible to install it indoors. All its components are selected and tested at the assembly stage. This eliminates the possibility of power drawdowns and other problems during the operation of the equipment.
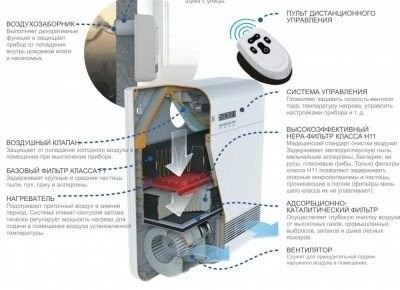
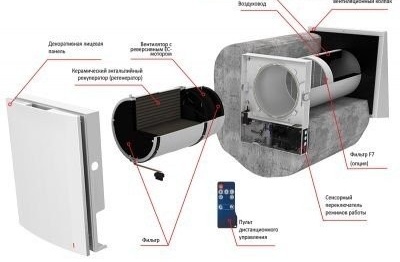
Compact ventilation system
This design is a supply valve, inside of which there is an air filter, an air heater and a fan. Its advantage is low cost, low power consumption, ease of installation. Compact systems vary in performance, device complexity, design and size.
There are installations with the ability to connect them with a centralized ventilation system. Conventionally, we can distinguish the following types:
- ventilator - air supply unit without automatic adjustment of temperature and power, ventilation of the room occurs only in the mode selected by the user;
- airgiver - ventilator with the ability to automatically maintain temperature;
- breather is a compact device in the form of a wall unit that adapts to changes in the external environment, which is equipped with a step-by-step air purification system and has a digital panel and a remote control.
Video: organization of supply and exhaust ventilation in a wooden house
The principle of supply ventilation
Air exchange in the supply ventilation system occurs due to the pressure difference inside and outside the room. This is a natural process that occurs without the participation of additional equipment. The circuit has both positive and negative points. If a residential building is located near a motorway or industrial enterprise, then the air taken from the outside will have a pronounced smell and contain a lot of harmful particles. To solve the problem in private buildings, it is recommended to use forced air supply duct type. In this case, air will be taken from the street with the help of special equipment.
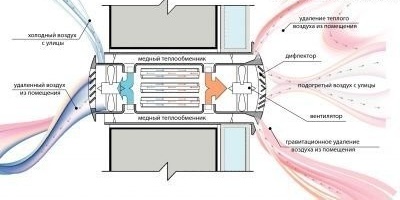
Fresh air ventilation
The principle of operation of the system with an air heater is similar to the above scheme. The air outside the room enters the ventilation duct due to natural draft or fan, is cleaned and enters the air heater. Two types of air heaters are distinguished depending on the heat carrier used:
- water - consists of heat transfer tubes and bimetallic grids; it is connected to the central water supply or heating equipment through a mixing unit;
- electric - a heating element acts as a heating element, the maximum temperature of the heated air is not more than 50 ° C with an air flow of up to 1.5 m / s.
It is recommended to use an electric air heater for apartments and private housing with an area of not more than 100 m2. In houses of a larger area, it is more economically feasible to install a water heater, since it will work in conjunction with underfloor heating and central heating.
Supply air heating
Air heating through ventilation with a heater is one of the modern ways of heating a home. Its feature is that heating, ventilation and air conditioning are connected into a single system. In the cold season, the air is heated in the duct system, and in the summer it cools to a comfortable temperature. This is a universal and economically viable approach for small and medium-sized homes.
If there is no underfloor heating or central heating system in the residential building, the air heating system, together with one of the listed options, will allow heating the house without any special financial costs.
Modern ventilation systems are equipped with automation that allows you to adjust the heating of the air to the desired temperature. For example, if tenants are absent for a long time at home, then the operation of the equipment can be transferred to an economical mode. This will allow heating the room to 10–12 ° C, and after returning to full operation, quickly warm the house to a comfortable temperature of 18–20 ° C.
Disadvantages of ventilation systems
Of the shortcomings of the supply ventilation can be identified:
- electricity consumption, which carries financial costs;
- high noise level;
- cost - the price of equipment and installation of ventilation directly depends on its type, design and the total capacity of the system.
Typing ventilation with a lot of equipment is unlikely to be possible to install with your own hands.Installation is carried out by specially trained personnel. Otherwise, the manufacturer (official dealer) may refuse the warranty.
Design and calculation of the ventilation system
Before buying equipment and components for ventilation installation, their technical parameters are calculated taking into account the size of the room - air performance, duct size. At the last stage, the appropriate equipment is selected: fan, air heater, etc.
Air performance
Air performance is measured in m³ / h and means how much air will pass through the room per unit of time. The calculation is carried out only for rooms where residents will be more than two hours a day. These include a bedroom, a nursery and a living room.
For corridors, kitchens, bathrooms and bathrooms, the calculation is not carried out. In these rooms, polluted air is discharged through exhaust valves.
This value is regulated by SNiP under the number 41–01–2003: for one person in rooms without natural ventilation, an air flow of at least 60 m³ / h should be established. The circulation of incoming air occurs due to single or double air exchange. This term means that within one hour in a ventilated room there will be a complete replacement of the air mass. Taking into account the performance and air exchange, the air flow is calculated:
- by the number of residents: L1 = N * LN, where L1 - ventilation performance in m³ / h, N - number of residents, LN - normalized air flow;
- in multiplicity: L2 = n * V, where L2 is the ventilation productivity in m³ / h, n is the air ratio, V is the volume of the room.
For example, for a living room of 10 m2 and a height of 2.3 m for one person L1 = 60 m³ / h, L2 = 46 m³ / h and ventilation with a capacity of 60 m³ / h is required.
Duct size
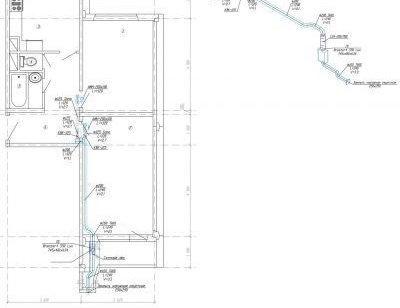
After determining the optimal ventilation power, they proceed to the calculation of the distribution channel system, consisting of air ducts, splitters, valves. At the stage of design work, it will be necessary to draw up a diagram of the ducting. It is optimal if several options are drawn up. Based on these drawings, the best solution is selected that allows, with the minimum length of the ventilation duct, to supply the required amount of air to a specific room.
The duct section is calculated by the formulas:
- calculated area: S1 = K * 2.778 / V, where K is the air flow through the ducts in m³ / h, V is the air flow rate in m / s, 2.778 is a constant coefficient;
- actual area for round ducts: S2 = π * D2 / 400, where π is 3.14, D is the diameter of the duct;
- actual area for square ducts: S3 = L * H / 100, where L and H are the width and height of the duct, respectively.
For standard size air ducts, you can use the table with the parameters already calculated.
Table: air flow for round and rectangular ducts
| Duct Parameters | Air consumption in m3/ h at air speed | ||||||
| Diameter of the round duct, mm | Dimensions of a rectangular duct, mm | The cross-sectional area of the duct, cm2 | 2 m / s | 3 m / s | 4 m / s | 5 m / s | 6 m / s |
| 80x90 | 72 | 52 | 78 | 104 | 130 | 156 | |
| 100 | 63x125 | 79 | 57 | 85 | 113 | 142 | 170 |
| 63x140 | 88 | 63 | 95 | 127 | 159 | 190 | |
| 110 | 90x100 | 90 | 65 | 97 | 130 | 162 | 194 |
| 80x140 | 112 | 81 | 121 | 161 | 202 | 242 | |
| 125 | 100x125 | 125 | 90 | 135 | 180 | 225 | 270 |
| 100x140 | 140 | 101 | 151 | 202 | 252 | 302 | |
| 140 | 125x125 | 156 | 112 | 169 | 225 | 281 | 337 |
| 90x200 | 180 | 130 | 194 | 281 | 324 | 389 | |
| 160 | 100x200 | 200 | 144 | 216 | 324 | 360 | 432 |
| 90x250 | 225 | 162 | 243 | 360 | 405 | 486 | |
| 180 | 160x160 | 256 | 184 | 276 | 369 | 461 | 553 |
| 90x315 | 283 | 204 | 306 | 408 | 510 | 612 | |
| 200 | 100x315 | 315 | 227 | 340 | 454 | 567 | 680 |
| 100x355 | 355 | 256 | 383 | 511 | 639 | 767 | |
| 225 | 160x250 | 400 | 288 | 432 | 576 | 720 | 864 |
| 125x355 | 443 | 319 | 479 | 639 | 799 | 958 | |
| 250 | 125x400 | 500 | 360 | 639 | 720 | 900 | 1080 |
| 200x315 | 630 | 454 | 680 | 907 | 1134 | 1361 | |
| 300 | 200x355 | 710 | 511 | 767 | 1022 | 1278 | 1533 |
| 160x450 | 720 | 518 | 778 | 1037 | 1296 | 1555 | |
| 315 | 250x315 | 787 | 567 | 850 | 1134 | 1417 | 1701 |
| 250x355 | 887 | 639 | 958 | 1278 | 1597 | 1917 | |
| 350 | 200x500 | 1000 | 720 | 1080 | 1440 | 1800 | 2160 |
| 250x450 | 1125 | 810 | 1215 | 1620 | 2025 | 2430 | |
| 400 | 250x500 | 1250 | 900 | 1350 | 1800 | 2250 | 2700 |
Heater power
To calculate the power, you need to know the minimum air temperature outside the building in the winter and the required air temperature at the outlet of the ventilation duct. Nominally 18 ° C is taken as a comfortable outlet temperature. The minimum temperature is selected taking into account the region. The power of the heater is calculated by the formula:
- P = T * L * 0.336 / 1000, where T is the temperature difference at the inlet to the ventilation duct and the outlet of the air heater, L is the ventilation system capacity in m³ / h, 0.336 is the heat capacity of the air without taking into account its humidity and temperature;
- taking into account the data from the example above: P = 44 * 120 * 0.336 / 1000, for supplying warm air with a temperature of 18 ° C to a living room of 10 m2 ventilation with an air heater with a power of about 1.8 kW will be required.
If the power exceeds the value of 5 kW, it is advisable to choose water equipment, since water from central / autonomous heating will be used for heating, which will reduce the cost of maintaining the system as a whole.
DIY ventilation system installation
The technology for installing fresh air ventilation depends on its capacity and design. Installation is best carried out at the stage of interior decoration of the building, since the ventilation will consist of a system of channels and equipment that are located under the ceiling or in the attic. Compact flats in the form of a ventilator-recuperator are ideal for apartments and houses of small area. The installation works in the supply and exhaust mode, and its installation can be done independently using a simple tool.
For installation work, you will need to prepare a puncher, screwdriver, hacksaw, screwdriver, household vacuum cleaner and scissors. Installation Technology:
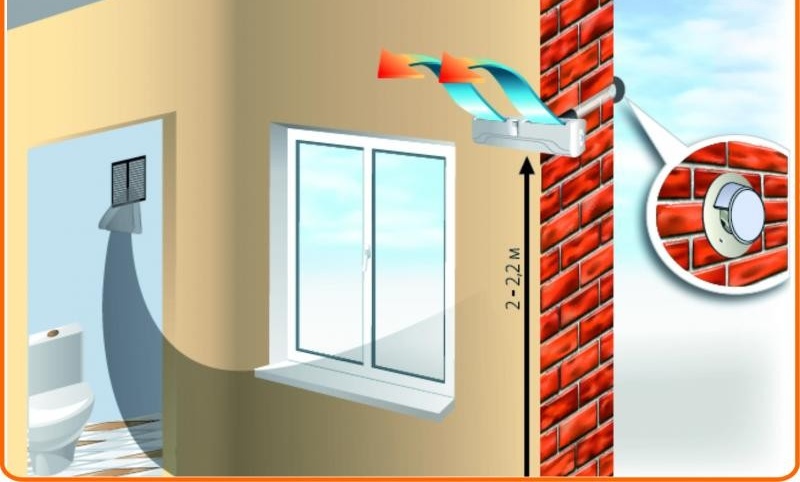
- Before starting installation, select the place where the ventilator will be installed. The device is recommended to be installed in the upper or lower part of the wall.
- Drill a hole in the wall at the selected location using a hammer drill. In this case, an air duct with a cross section of 150 mm is used, so the diameter of the hole should not exceed 160 mm.
- If the installation of the ventilator is carried out at the stage of rough finishing, it is more expedient to make wiring of a hidden type. A power cable with a core thickness of 1–1.5 mm is enough to power the device.
- Insert a plastic duct into the hole in the wall and adjust the length so that the pipe protrudes 1-3 mm outside the room.
- After trimming, insert the duct into the channel. From the side of the street, on the front of the building, attach the housing from the protective cap. To do this, drill four holes and hammer in the nails included in the delivery.
- From the side of the room, attach a cardboard template to the hole and make markings for the installation of the indoor unit.
- Before mounting the unit, fill the space between the duct and the duct with foam. After solidification, cut off its excess with a sharp knife flush with the wall.
- To fasten the unit, remove the front panel, which is fixed on the latches on the sides of the device, and the left protective cover by unscrewing the two screws.
- After that, you can proceed to installing the back of the indoor unit: skip the power cable if hidden wiring was previously done. For open wiring, a special plug is provided at the bottom of the unit.
- Attach the back of the block to the wall according to the previously applied marking and screw it onto four screws. Then connect the cable to the terminals, according to the diagram in the instructions. Attach the protective cover to its original position.
- Install the cartridge in the duct. To connect it to the board, connect the connector to the contacts on the right side of the unit. After that, install the front of the indoor unit.
- Install the noise insulator from the street side: twist the material into a roll along the diameter of the air duct and push it into the ventilation duct until it stops, and cut off the protruding part taking into account the edges of the air duct and install the sound insulator sized back into the air duct.
- Fasten the outer ventilation hood and fine-tune the device. To do this, remove the rubber plug that hides the on / off switches. Set up according to the decryption sticker located to the left of the switches.
After adjustment, the indoor unit is closed and the system is checked for operability.
Video: installation of a supply ventilation unit for private housing
System maintenance
Supply ventilation is maintained at least twice a year:
- in the fall (before the onset of the first frost);
- in spring (after the average daily temperature is 3–5 ° C).
During this, a full diagnosis of the system’s performance is carried out - an external examination of the equipment, checking the voltage at the nodes of the electrical connections and cleaning the filtration system. The cost of servicing ventilation for a private house depends on its capacity.
Modern ventilation systems designed for use in the private sector create comfortable living conditions. Before buying and installing equipment, consult with specialists. This will help not only save your own money, but also less often maintain the system during its operation.